Addition Of D-Sorbitol Improves The Usability Of Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Devices
- PMID: 31576103
- PMCID: PMC6769236
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S218675
Addition Of D-Sorbitol Improves The Usability Of Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Devices
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effects of D-sorbitol addition on changes in the extrusion force of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices (OVDs).
Methods: OVD formulations; the mixtures of 3% hyaluronic acid (HA) and 4% chondroitin sulfate (CS) containing 0%, 0.5%, or 1.0% D-sorbitol were prepared. Each prefilled syringe of OVD was stored at room temperature for 0, 15, 30, 60, or 120 mins after a small amount of viscoelastic agent was discharged from the needle. The extrusion force values (kgf) of these OVDs when reused after storage were measured with a texture analyzer. Moreover, 10 healthy adults (5 men and 5 women) used a pinch sensor to measure the extrusion force values for the HA/CS combination without D-sorbitol which was stored in the above manner, and used a 4-step scale to score the usability of OVD.
Results: For the HA/CS combination without D-sorbitol, the extrusion force value was increased from its initial value (storage duration, 0 min) as storage duration increased. However, for the HA/CS combination containing 0.5% or 1.0% D-sorbitol, this value remained almost unchanged over time. Likewise, the pinch sensor-determined extrusion force values of HA/CS combination without D-sorbitol increased, depending on storage duration.
Conclusion: The addition of D-sorbitol to viscoelastic agent may suppress the needle clogging that occurs with OVD storage, and may improve the usability of OVDs during surgery.
Keywords: cataract surgery; extrusion force; ophthalmic viscosurgical device; vitreous surgery.
© 2019 Watanabe et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

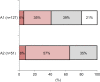
 ; I do not store OVDs but have experienced needle clogging,
; I do not store OVDs but have experienced needle clogging,  ; I have experienced needle clogging due to storage,
; I have experienced needle clogging due to storage,  ; I sometimes store OVDs but have not experienced needle clogging, □; I have not experienced needle clogging because I do not store OVDs. A2: Answer to the Q2 “During cataract surgery or vitreous surgery, when applying viscoelastic agent to the corneal surface, how do you deal with needle clogging?”
; I sometimes store OVDs but have not experienced needle clogging, □; I have not experienced needle clogging because I do not store OVDs. A2: Answer to the Q2 “During cataract surgery or vitreous surgery, when applying viscoelastic agent to the corneal surface, how do you deal with needle clogging?”  ; Immersed the needle tip in physiological saline,
; Immersed the needle tip in physiological saline,  ; Immersed the needle tip in BSS,
; Immersed the needle tip in BSS,  ; Others. Abbreviations: OVD, ophthalmic viscosurgical devices; BSS, balanced salt solution.
; Others. Abbreviations: OVD, ophthalmic viscosurgical devices; BSS, balanced salt solution.
 ; no D-sorbitol,
; no D-sorbitol,  ; 0.5% D-sorbitol, and
; 0.5% D-sorbitol, and  ; 1.0% D-sorbitol. The relative extrusion force (%) is presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Effect of soaking the needle in PBS on the extrusion force of HA/CS-A exposed to the open air for 60 mins (E). Treatment: the needle tip was soaked in PBS after exposure to the open air for 60 mins. Non-treatment: the needle tip was not soaked in PBS. The relative extrusion force (%) is presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). Abbreviations: OVD, ophthalmic viscosurgical devices; HA, hyaluronic acid; CS, chondroitin sulfate; kgf, kilogram-force; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.
; 1.0% D-sorbitol. The relative extrusion force (%) is presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Effect of soaking the needle in PBS on the extrusion force of HA/CS-A exposed to the open air for 60 mins (E). Treatment: the needle tip was soaked in PBS after exposure to the open air for 60 mins. Non-treatment: the needle tip was not soaked in PBS. The relative extrusion force (%) is presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). Abbreviations: OVD, ophthalmic viscosurgical devices; HA, hyaluronic acid; CS, chondroitin sulfate; kgf, kilogram-force; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.Similar articles
-
[Clinical Functionality of Dispersive OVDs: Improvement of One of the Properties of 3% Hyaluronic Acid and 4% Chondroitin Sulfate Combination].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022;142(4):401-411. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.21-00208. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 35370196 Japanese.
-
D-sorbitol can keep the viscosity of dispersive ophthalmic viscosurgical device at room temperature for long term.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 14;9(1):16815. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53390-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31727999 Free PMC article.
-
Prefilled syringes and usability of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices.Clin Ophthalmol. 2014 Sep 4;8:1697-702. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S67689. eCollection 2014. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25228786 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal Outcomes Following Cataract Surgery Using Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Devices Composed of Chondroitin Sulfate-Hyaluronic Acid: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul 24;17:2083-2096. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S419863. eCollection 2023. Clin Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37521151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ophthalmic Viscosurgical Devices (OVDs) in Challenging Cases: a Review.Ophthalmol Ther. 2021 Dec;10(4):831-843. doi: 10.1007/s40123-021-00403-9. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Ophthalmol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34617249 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

