High levels of serum glycans monovalent IgG immune complexes detected by dissociative ELISA in experimental visceral leishmaniasis
- PMID: 31576564
- PMCID: PMC6856933
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.13118
High levels of serum glycans monovalent IgG immune complexes detected by dissociative ELISA in experimental visceral leishmaniasis
Abstract
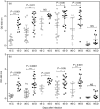
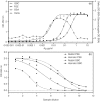
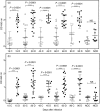
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is epidemic in Brazil with an increasing incidence of human cases and canine reservoirs, with host hypergammaglobulinemia. Conventional enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (cELISA) based on several parasitic antigens is the main method for diagnosis and indication of treatment. Dissociative ELISA (dELISA) uses acidic treatment to free immunoglobulin G (IgG) from immune complexes, and its use revealed a significant positive fraction of suspected cases with negative serology. Looking for small molecules or haptens that block IgG antibodies, we purified by molecular exclusion chromatography, 1000-3000 MW molecules from promastigote soluble extract, mostly oligosaccharides comprising 6-13 sugar residues using MALDI-TOF analysis. Glycan-BSA complex (GBC) was constructed by conjugating promastigote glycans to BSA molecules, allowing their use in the solid support in cELISA or dELISA. Sera from experimentally infected hamsters showed higher levels of blocked monomeric IgG during infection, mostly against GBC, which was also present in lower concentrations in the promastigote soluble extract dELISA. Those data show that most of the specific monomeric IgG in serum are blocked by haptens composed by glycans produced by the parasite, better detected in the high dilution of sera in the dELISA assays. dELISA is a useful technique for detecting blocked monomeric antibodies that could have difficult clearance from blood, which could result in hypergammaglobulinemia.
Keywords: Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum chagasi; glycan; hapten; hypergammaglobulinemia; immune complexes.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum antibodies blocked by glycan antigens in canine visceral leishmaniasis serology are mostly IgA immune complexes.Parasitology. 2021 Oct;148(12):1509-1515. doi: 10.1017/S0031182021001189. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Parasitology. 2021. PMID: 34218828 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding hypergammaglobulinemia in experimental or natural visceral leishmaniasis.Parasite Immunol. 2024 Jan;46(1):e13021. doi: 10.1111/pim.13021. Parasite Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38275197
-
A simple immune complex dissociation ELISA for leishmaniasis: standardization of the assay in experimental models and preliminary results in canine and human samples.Acta Trop. 2013 Feb;125(2):128-36. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.10.010. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Acta Trop. 2013. PMID: 23123344
-
Early high avidity specific IgG production in experimental hamster visceral leishmaniasis.Parasitol Res. 2020 Nov;119(11):3881-3885. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06851-9. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32797264
-
Indirect Evidence of Circulating Parasite Hapten Immune Complexes in Visceral Leishmaniasis.J Appl Lab Med. 2019 Nov;4(3):404-409. doi: 10.1373/jalm.2018.028282. Epub 2019 Jul 3. J Appl Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 31659077
Cited by
-
Serum antibodies blocked by glycan antigens in canine visceral leishmaniasis serology are mostly IgA immune complexes.Parasitology. 2021 Oct;148(12):1509-1515. doi: 10.1017/S0031182021001189. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Parasitology. 2021. PMID: 34218828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Leishmaniasis. [cited 30 April 2019]. URL http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs375/en/ [accessed on 25 July 2019]
-
- Kevric I, Cappel MA, Keeling JH. New world and old world Leishmania infections: a practical review. Dermatol Clin 2015; 33:579–93. - PubMed
-
- Saporito L, Giammanco GM, De Grazia S, Colomba C. Visceral leishmaniasis: host–parasite interactions and clinical presentation in the immunocompetent and in the immunocompromised host. Int J Infect Dis 2013; 17:e572–6. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadhyay S, Mandal C. Glycobiology of Leishmania donovani . Indian J Med Res 2006; 123:203–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

