NosP Modulates Cyclic-di-GMP Signaling in Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 31576744
- PMCID: PMC6812680
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00618
NosP Modulates Cyclic-di-GMP Signaling in Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
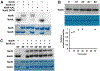
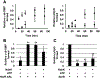
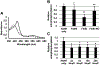
Biofilms form when bacteria adhere to a surface and secrete an extracellular polymeric substance. Bacteria embedded within a biofilm benefit from increased resistance to antibiotics, host immune responses, and harsh environmental factors. Nitric oxide (NO) is a signaling molecule that can modulate communal behavior, including biofilm formation, in many bacteria. In many cases, NO-induced biofilm dispersal is accomplished through signal transduction pathways that ultimately lead to a decrease in intracellular cyclic-di-GMP levels. H-NOX (heme nitric oxide/oxygen binding domain) proteins are the best characterized bacterial NO sensors and have been implicated in NO-mediated cyclic-di-GMP signaling, but we have recently discovered a second family of NO-sensitive proteins in bacteria named NosP (NO sensing protein); to date, a clear link between NosP signaling and cyclic-di-GMP metabolism has not been established. Here we present evidence that NosP (Lpg0279) binds to NO and directly affects cyclic-di-GMP production from two-component signaling proteins Lpg0278 and Lpg0277 encoded within the NosP operon. Lpg0278 and Lpg0277 are a histidine kinase and cyclic-di-GMP synthase/phosphodiesterase, respectively, that have already been established as being important in regulating Legionella pneumophila cyclic-di-GMP levels; NosP is thus implicated in regulating cyclic-di-GMP in L. pneumophila.
Figures

References
-
- Bruggemann H, Hagman A, Jules M, Sismeiro O, Dillies M-A, Gouyette C, Kunst F, Steinert M, Heuner K, Coppee J-Y & Buchrieser C (2006) Virulence strategies for infecting phagocytes deduced from the in vivo transcriptional program of Legionella pneumophila. Cell. Microbiol 8, 1228–1240. - PubMed
-
- Declerck P, Behets J, Margineanu A, van Hoef V, De Keersmaecker B & Ollevier F (2009) Replication of Legionella pneumophila in biofilms of water distribution pipes. Microbiol. Res 164, 593–603. - PubMed
-
- Pécastaings S, Bergé M, Dubourg KM & Roques C (2010) Sessile Legionella pneumophila is able to grow on surfaces and generate structured monospecies biofilms. Biofouling 26, 809–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

