Formulation and evaluation of itraconazole liposomes for Hedgehog pathway inhibition
- PMID: 31576768
- PMCID: PMC7113120
- DOI: 10.1080/08982104.2019.1668011
Formulation and evaluation of itraconazole liposomes for Hedgehog pathway inhibition
Abstract
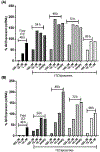
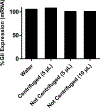
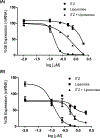
Itraconazole (ITZ) is an FDA-approved antifungal agent that has recently been explored for novel biological properties. In particular, ITZ was identified as a potent inhibitor of the hedgehog (Hh) pathway, a cell signalling pathway that has been linked to a variety of cancers and accounts for ∼25% of paediatric medulloblastoma (MB) cases. To date, there is not a targeted therapeutic option for paediatric MB, resulting in long-term side effects such as hormone deficiency, organ damage and secondary cancers. A primary obstacle for developing targeted therapy for brain ailments is the presence of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which protects the brain from potentially harmful substances. Due to its size and hydrophobicity, ITZ does not penetrate the BBB. Alternatively, liposomes are being increasingly used within the clinic to increase drug bioavailability, target specificity and BBB permeability. With this in mind, we have successfully developed ITZ-containing liposomes with an optimal size for BBB penetration (<100 nm) and encapsulation efficiency (∼95%) by utilizing a continuous manufacturing approach-turbulent coaxial jet in co-flow. Our preliminary in vitro data demonstrate that these liposomes inhibit the Hh pathway, albeit at a reduced level in comparison to free ITZ. (196/250 words).
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; Hedgehog; cancer; drug repurposing; itraconazole; liposome; medulloblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aghaloo TL, Amantea CM, Cowan CM, Richardson JA, Wu BM, Parhami F, and Tetradis S, 2007. Oxysterols enhance osteoblast differentiation in vitro and bone healing in vivo. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 25 (11), 1488–1497. - PubMed
-
- Amakye D, Jagani Z, and Dorsch M, 2013. Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nature Medicine, 19 (11), 1410–1422. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J and Thérond PP, 2013. The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 14 (7), 416–429. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
