Monoclonal Antibody to Marinobufagenin Downregulates TGFβ Profibrotic Signaling in Left Ventricle and Kidney and Reduces Tissue Remodeling in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
- PMID: 31576777
- PMCID: PMC6818028
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012138
Monoclonal Antibody to Marinobufagenin Downregulates TGFβ Profibrotic Signaling in Left Ventricle and Kidney and Reduces Tissue Remodeling in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Monoclonal Antibody to Marinobufagenin Downregulates TGFβ Profibrotic Signaling in Left Ventricle and Kidney and Reduces Tissue Remodeling in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Oct 4;11(19):e020832. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.020832. Epub 2022 Sep 29. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 36172940 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
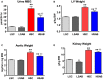
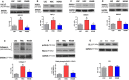
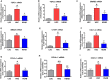
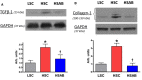
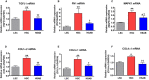
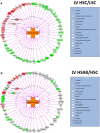
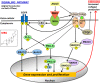
Background Elevated levels of an endogenous Na/K-ATPase inhibitor marinobufagenin accompany salt-sensitive hypertension and are implicated in cardiac fibrosis. Immunoneutralization of marinobufagenin reduces blood pressure in Dahl salt-sensitive (Dahl-S) rats. The effect of the anti-marinobufagenin monoclonal antibody on blood pressure, left ventricular (LV) and renal remodeling, and gene expression were investigated in hypertensive Dahl-S rats. Methods and Results Dahl-S rats were fed high NaCl (8%, HS; n=14) or low NaCl (0.1%, LS; n=14) diets for 8 weeks. Animals were administered control antibody (LS control antibody, LSC; HS control antibody, HSC; n=7 per group) or anti-marinobufagenin antibody once on week 7 of diet intervention (n=7 per group). Levels of marinobufagenin, LV, and kidney mRNAs and proteins implicated in profibrotic signaling were assessed. Systolic blood pressure was elevated (211±8 versus 133±3 mm Hg, P<0.01), marinobufagenin increased 2-fold in plasma (P<0.05) and 5-fold in urine (P<0.01), LV and kidney weights increased, and levels of LV collagen-1 rose 3.5-fold in HSC versus LSC. Anti-marinobufagenin antibody treatment decreased systolic blood pressure by 24 mm Hg (P<0.01) and reduced organ weights and level of LV collagen-1 (P<0.01) in hypertensive Dahl salt-sensitive rats with anti-marinobufagenin antibody versus HSC. The expression of genes related to transforming growth factor-β-dependent signaling was upregulated in the left ventricles and kidneys in HSC versus LSC groups and became downregulated following administration of anti-marinobufagenin antibody to hypertensive Dahl-S rats. Marinobufagenin also activated transforming growth factor-β signaling in cultured ventricular myocytes from Dahl-S rats. Conclusions Immunoneutralization of heightened marinobufagenin levels in hypertensive Dahl-S rats resulted in a downregulation of genes implicated in transforming growth factor-β pathway, which indicates that marinobufagenin is an activator of profibrotic transforming growth factor-β-dependent signaling in salt-sensitive hypertension.
Keywords: Dahl salt‐sensitive hypertension; cardiac hypertrophy; marinobufagenin; monoclonal antibody; transforming growth factor.
Figures

References
-
- Folkow B. Physiological aspects of primary hypertension. Physiol Rev. 1982;62:347–504. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger MH, Miller JZ, Luft FC, Grim CE, Fineberg NS. Definitions and characteristics of sodium sensitivity and blood pressure resistance. Hypertension. 1986;8:II127–II134. - PubMed
-
- Wasserstrom JA, Aistrup GL. Digitalis: new actions for an old drug. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289:H1781–H1793. - PubMed
-
- de Wardener HE, Clarkson EM. Concept of natriuretic hormone. Physiol Rev. 1985;65:658–759. - PubMed
-
- Fedorova OV, Talan MI, Agalakova NI, Lakatta EG, Bagrov AY. Endogenous ligand of alpha(1) sodium pump, marinobufagenin, is a novel mediator of sodium chloride–dependent hypertension. Circulation. 2002;105:1122–1127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

