C-type lectin family XIV members and angiogenesis
- PMID: 31579078
- PMCID: PMC6757257
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10760
C-type lectin family XIV members and angiogenesis
Abstract
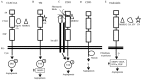
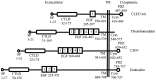
The growth and metastasis of tumors is dependent on angiogenesis. C-type lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins with a diverse range of functions. The C-type lectin family XIV members are transmembrane glycoproteins, and all four members of this family have been reported to regulate angiogenesis, although the detailed mechanism of action has yet to be completely elucidated. They interact with extracellular matrix proteins and mediate cell-cell adhesion by their lectin-like domain. The aim of the present study was to summarize the available information on the function and mechanism of C-type lectin family XIV in angiogenesis and discuss their potential as targets for cancer therapy.
Keywords: C-type lectin family XIV; CD93; CLEC14A; angiogenesis; endosialin; thrombomodulin.
Copyright © 2019, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
