Development, optimization, standardization, and validation of a simple in-house agar gradient method to determine minimum inhibitory concentration of vancomycin for Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 31579244
- PMCID: PMC6771310
- DOI: 10.4103/JLP.JLP_11_19
Development, optimization, standardization, and validation of a simple in-house agar gradient method to determine minimum inhibitory concentration of vancomycin for Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Background: The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute recommends reporting minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of vancomycin for Staphylococcus aureus. Commercial MIC strips are expensive, and the traditional broth microdilution method is cumbersome. With this background, we attempted to develop and standardize an in-house agar gradient method to determine MIC values of vancomycin for S. aureus.
Objectives: To develop and validate an in-house vancomycin MIC strip, based on simple agar gradient method for S. aureus as per bioassay development guidelines.
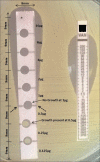
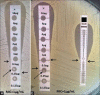
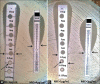
Materials and methods: Filter paper gradient strips were made in house and impregnated with varying concentrations of vancomycin to create an antibiotic gradient. During standardization, MICs of ninety clinical strains of S. aureus and ATCC 29213 were tested by the broth microdilution and commercial strip followed by the in-house strip. During the validation stage, MICs of ninety different clinical strains of S. aureus and ATCC 29213 were determined by the in-house strip followed by MIC detection by broth microdilution and commercial strips. A reading of more than ± 1log2 dilution compared with broth microdilution was considered as an outlier.
Results: During the initial stage, there were 7/90 outliers in the clinical strains, and no outliers were seen with the ATCC 29213 control strain. Corrective action included increasing precaution during the antibiotic impregnation on the strip. During validation stage, only 4/90 outliers were observed in the clinical strains. The commercial strips had 29/90 among clinical and 15/30 outliers in the control strain during the prevalidation phase. Despite maintaining cold chain during the validation phase, the outliers for commercial strip were 18/90 and 4/30 for clinical and control strains, respectively.
Conclusion: Reporting vancomycin MIC for S. aureus may be attempted using the in-house method after validating it with a gold standard broth microdilution method and quality control as per protocol.
Keywords: AMR; Epsilometer test; antimicrobial testing; in-house agar gradient method; minimum inhibitory concentration; vancomycin.
Copyright: © 2019 Journal of Laboratory Physicians.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Daptomycin bactericidal activity and correlation between disk and broth microdilution method results in testing of Staphylococcus aureus strains with decreased susceptibility to vancomycin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jul;50(7):2330-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01491-05. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16801409 Free PMC article.
-
Broth Microdilution and Gradient Diffusion Strips vs. Reference Agar Dilution Method: First Evaluation for Clostridiales Species Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Aug 12;10(8):975. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080975. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439025 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of microdilution and standard agar dilution method for determining Penicillin resistance among S.pneumoniae.J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2014 May-Aug;12(27):112-5. J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2014. PMID: 25575004
-
Comparison of agar dilution and antibiotic gradient strip test with broth microdilution for susceptibility testing of swine Brachyspira species.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2016 Mar;28(2):133-43. doi: 10.1177/1040638716629154. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2016. PMID: 26965233
-
[Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms to vancomycin, gemtamicin and rifampin].Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2010 Apr;59(2):80-7. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2010. PMID: 20586169 Slovak.
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Approved Standard. 10th ed. Wayne, USA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2015. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that grow Aerobically; pp. M07–A10.
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Twenty Fifth Informational Supplement. Wayne, USA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2015. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; pp. M100–S25.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

