Colloquium: Ionic phenomena in nanoscale pores through 2D materials
- PMID: 31579274
- PMCID: PMC6774369
- DOI: 10.1103/RevModPhys.91.021004
Colloquium: Ionic phenomena in nanoscale pores through 2D materials
Abstract
Ion transport through nanopores permeates through many areas of science and technology, from cell behavior to sensing and separation to catalysis and batteries. Two-dimensional materials, such as graphene, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), are recent additions to these fields. Low-dimensional materials present new opportunities to develop filtration, sensing, and power technologies, encompassing ion exclusion membranes, DNA sequencing, single molecule detection, osmotic power generation, and beyond. Moreover, the physics of ionic transport through pores and constrictions within these materials is a distinct realm of competing many-particle interactions (e.g., solvation/dehydration, electrostatic blockade, hydrogen bond dynamics) and confinement. This opens up alternative routes to creating biomimetic pores and may even give analogues of quantum phenomena, such as quantized conductance, in the classical domain. These prospects make membranes of 2D materials - i.e., 2D membranes - fascinating. We will discuss the physics and applications of ionic transport through nanopores in 2D membranes.
Figures


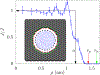
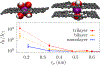


Similar articles
-
Single-Layer Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanopores as High-Performance Ionic Gradient Power Generators.Small. 2024 Apr;20(16):e2306018. doi: 10.1002/smll.202306018. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Small. 2024. PMID: 38041449
-
Two-dimensional nanopores and nanoporous membranes for ion and molecule transport.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019 Feb;55:124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30321759 Review.
-
Two-Dimensional Nanofluidic Membranes toward Harvesting Salinity Gradient Power.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Nov 16;54(22):4154-4165. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00431. Epub 2021 Oct 31. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34719227
-
Nanopores in Graphene and Other 2D Materials: A Decade's Journey toward Sequencing.ACS Nano. 2021 Dec 28;15(12):18848-18864. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c07960. Epub 2021 Nov 29. ACS Nano. 2021. PMID: 34841865 Review.
-
Geometrical Effect in 2D Nanopores.Nano Lett. 2017 Jul 12;17(7):4223-4230. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b01091. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Nano Lett. 2017. PMID: 28592108
Cited by
-
Ionic heat dissipation in solid-state pores.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 11;8(6):eabl7002. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl7002. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35148181 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects of Observing Ionic Coulomb Blockade in Artificial Ion Confinements.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Dec 18;22(12):1430. doi: 10.3390/e22121430. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33353100 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore sensing: A physical-chemical approach.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021 Sep 1;1863(9):183644. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183644. Epub 2021 May 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021. PMID: 33989531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Covalent Benzenesulfonic Functionalization of a Graphene Nanopore for Enhanced and Selective Proton Transport.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2024 Feb 21;128(8):3514-3524. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.3c07406. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38445014 Free PMC article.
-
Tunable Anion-Selective Transport through Monolayer Graphene and Hexagonal Boron Nitride.ACS Nano. 2020 Mar 24;14(3):2729-2738. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b08168. Epub 2020 Jan 8. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 31891480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham J, Vasu KS, Williams CD, Gopinadhan K, Su Y, Cherian CT, Dix J, Prestat E, Haigh SJ, Grigorieva IV, et al. (2017), Nat. Nanotech 12, 546. - PubMed
-
- Ackerman MJ, and Clapham DE (1997), N. Engl. J. Med 336, 1575. - PubMed
-
- Aguilella-Arzo M, Aguilella VM, and Eisenberg RS (2005), Eur. Biophys. J 34, 314. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
