Effects of ABT-737 combined with irradiation treatment on uterine cervical cancer cells
- PMID: 31579427
- PMCID: PMC6757300
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10755
Effects of ABT-737 combined with irradiation treatment on uterine cervical cancer cells
Abstract
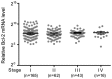
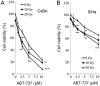
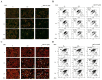
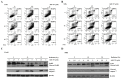
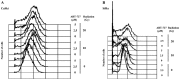
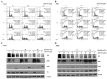
The aim of the present study was to examine the role of ABT-737, an inhibitor of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), in enhancing the effect of irradiation on uterine cervical cancer. Based on The Cancer Genomic Atlas (TCGA), Bcl-2 mRNA expression was associated with the Tumor-Node-Metastasis stage of cervical cancer. Therefore, it was hypothesized that Bcl-2 inhibition may decrease the progression of cervical cancer. ABT-737 was added to irradiation treatment to evaluate its effectiveness in inhibiting cancer cell progression. SiHa and CaSki cervical cancer cells were selected for in vitro assays. Patients with advanced stage III uterine cancer had slightly increased mRNA expression levels of Bcl-2 compared with patients with stage I cancer, although the difference was not significant. ABT-737 and radiation administration induced a synergistic cytotoxic effect based on the MTT assay and flow cytometry results, where an increase in apoptosis was observed. The apoptotic percentages were significantly increased in the cells treated with a combination of ABT-737 and irradiation. Loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and gain of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were detected by flow cytometry in CaSki and SiHa cells treated with ABT-737 and radiation. Additionally, the protein expression levels of the cleaved forms of poly ADP ribose polymerase and caspase-7 were increased following the combined treatment. In conclusion, ABT-737 and irradiation may induce apoptosis via loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and a ROS-dependent apoptotic pathway in CaSki and SiHa cells. The present study indicates that ABT-737 may be a potential irradiation adjuvant when treating cervical cancer.
Keywords: ABT-73; B-cell lymphoma 2; apoptosis; irradiation; mitochondrial membrane potential; uterine cervical cancer.
Copyright © 2019, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Application of Arsenic Trioxide in Ameliorating ABT-737 Target Therapy on Uterine Cervical Cancer Cells through Unique Pathways in Cell Death.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 31;12(1):108. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010108. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31906234 Free PMC article.
-
Co-inhibition of BCL-XL and MCL-1 with selective BCL-2 family inhibitors enhances cytotoxicity of cervical cancer cell lines.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020 Apr 22;22:100756. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100756. eCollection 2020 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020. PMID: 32346617 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of synergy of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide and ABT-737 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines: Mcl-1 inactivation.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008 Apr 16;100(8):580-95. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn076. Epub 2008 Apr 8. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008. PMID: 18398104
-
Bcl-2 protects TK6 cells against hydroquinone-induced apoptosis through PARP-1 cytoplasm translocation and stabilizing mitochondrial membrane potential.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2018 Jan;59(1):49-59. doi: 10.1002/em.22126. Epub 2017 Aug 26. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2018. PMID: 28843007
-
[Bcl-2 inhibitor ABT-737 enhances the cisplatin-induced apoptosis in breast cancer T47D cells].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011 Dec;33(12):891-5. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22340096 Chinese.
Cited by
-
BH3-mimetics: recent developments in cancer therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Nov 9;40(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02157-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34753495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Therapy with MiRNA-Mediated Targeting of Mcl-1 Promotes the Sensitivity of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Treatment with ABT-737.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Mar 1;21(3):675-681. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.3.675. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32212793 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Arsenic Trioxide in Ameliorating ABT-737 Target Therapy on Uterine Cervical Cancer Cells through Unique Pathways in Cell Death.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 31;12(1):108. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010108. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31906234 Free PMC article.
-
A recent development of new therapeutic agents and novel drug targets for cancer treatment.SAGE Open Med. 2021 Dec 23;9:20503121211067083. doi: 10.1177/20503121211067083. eCollection 2021. SAGE Open Med. 2021. PMID: 34992782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual Akt and Bcl-2 inhibition induces cell-type specific modulation of apoptotic and autophagic signaling in castration resistant prostate cancer cell lines.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Dec;48(12):7755-7765. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06786-z. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34647221
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
