Pharmacological evidence for lithium-induced neuroprotection against methamphetamine-induced neurodegeneration via Akt-1/GSK3 and CREB-BDNF signaling pathways
- PMID: 31579440
- PMCID: PMC6760490
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.30855.7442
Pharmacological evidence for lithium-induced neuroprotection against methamphetamine-induced neurodegeneration via Akt-1/GSK3 and CREB-BDNF signaling pathways
Abstract
Objectives: Neurodegeneration is an outcome of Methamphetamine (METH) abuse. Studies have emphasized on the neuroprotective properties of lithium. The current study is designed towards evaluating the role of Akt-1/GSK3 and CREB-BDNF signaling pathways in mediating lithium neuroprotection against METH-induced neurodegeneration in rats.
Materials and methods: Sixty adult male rats were randomly divided into five groups: control group (received 0.7 ml normal saline per rat for 28 days), METH group (given 10 mg/kg of METH intraperitoneally for 28 days), groups 3, 4, and 5 (given METH (10 mg/kg) and lithium (75, 150, and 300 mg/kg intraperitoneally, individually for 28 days). Morris water maze (MWM) was used to assess mental functions. In addition to hippocampal neurodegeneration, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), cAMP response element binding (CREB), Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), and Protein kinase B (Akt-1) were assessed in isolated hippocampus.
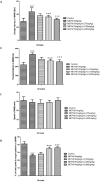
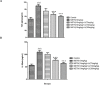
Results: METH abuse caused marked disorders in learning and memory that were dramatically improved with various doses of lithium. Furthermore, METH increased lipid peroxidation and the levels of oxidized form of interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), glutathione (GSSG), Bax, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and GSK3, while attenuating the extent of glutathione (reduced form (GSH)), P-CREB, Bcl-2, BDNF, and Akt-1 in the hippocampus. Moreover, METH declined superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione reductase (GR), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity in the hippocampus. Conversely, lithium attenuated METH-stimulated apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation; while improving the extent of BDNF and P-CREB.
Conclusion: Probably lithium possesses neuroprotection against METH-stimulated neurodegeneration in the hippocampus via Akt-1/GSK3β and CREB/BDNF signaling pathways.
Keywords: Akt; BDNF; CREB; GSK3; Lithium; Methamphetamine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective Properties of Minocycline Against Methylphenidate-Induced Neurodegeneration: Possible Role of CREB/BDNF and Akt/GSK3 Signaling Pathways in Rat Hippocampus.Neurotox Res. 2022 Jun;40(3):689-713. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00454-7. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 35446003
-
Crocin Acting as a Neuroprotective Agent against Methamphetamine-induced Neurodegeneration via CREB-BDNF Signaling Pathway.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Spring;18(2):745-758. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.2393. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 31531058 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of metformin against methamphetamine induced anxiety, depression, cognition impairment and neurodegeneration in rat: The role of CREB/BDNF and Akt/GSK3 signaling pathways.Neurotoxicology. 2019 May;72:74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Neurotoxicology. 2019. PMID: 30742852
-
Is lithium neuroprotective? An updated mechanistic illustrated review.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Feb;37(1):4-30. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12826. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35996185 Review.
-
Novel Insight to Neuroprotective Potential of Curcumin: A Mechanistic Review of Possible Involvement of Mitochondrial Biogenesis and PI3/Akt/ GSK3 or PI3/Akt/CREB/BDNF Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Cell Med. 2020 Winter;9(1):1-32. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.9.1.1. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2020. PMID: 32832482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates methamphetamine (METH)-induced neurotoxicity through the NR2B/ERK/CREB/BDNF signalings in vitro and in vivo models.J Ginseng Res. 2022 May;46(3):426-434. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.07.005. Epub 2021 Jul 14. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 35600772 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Selegiline Agent Methamphetamine-Prompted Mood-Related Behavior Disorder Mediated Via 5-HT2 and D2 Receptors.Int J Prev Med. 2023 Jun 22;14:78. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_42_22. eCollection 2023. Int J Prev Med. 2023. PMID: 37855005 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology to investigate the pharmacological mechanisms of muscone in Xingnaojing injections for the treatment of severe traumatic brain injury.PeerJ. 2021 Jul 20;9:e11696. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11696. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34322321 Free PMC article.
-
ω-3PUFAs Improve Cognitive Impairments Through Ser133 Phosphorylation of CREB Upregulating BDNF/TrkB Signal in Schizophrenia.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Jul;17(3):1271-1286. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00859-w. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 32367475 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent effects of H2S on post-traumatic stress disorder in adolescent and adult mice.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Jun 9;16:1546737. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1546737. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40551819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darke S, Darke S, Kaye S, Darke S, Kaye S, McKetin R, et al. Major physical and psychological harms of methamphetamine use. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2008;27:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang G-J, Fowler JS, Leonido-Yee M, Franceschi D, et al. Association of dopamine transporter reduction with psychomotor impairment in methamphetamine abusers. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:377–382. - PubMed
-
- Thrash B, Karuppagounder SS, Uthayathas S, Suppiramaniam V, Dhanasekaran M. Neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine. Neuroch Res. 2010;35:171–179. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
