Effects of Euterpe oleracea to Enhance Learning and Memory in a Conditioned Nicotinic and Muscarinic Receptor Response Paradigm by Modulation of Cholinergic Mechanisms in Rats
- PMID: 31580752
- PMCID: PMC7185363
- DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2018.0197
Effects of Euterpe oleracea to Enhance Learning and Memory in a Conditioned Nicotinic and Muscarinic Receptor Response Paradigm by Modulation of Cholinergic Mechanisms in Rats
Abstract
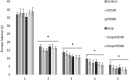
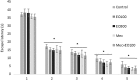
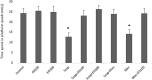
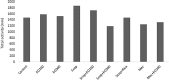
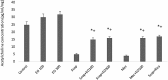
Euterpe oleracea (EO) includes a large number of polyphenolic compounds such as phenolics, flavonoids, and anthocyanins that have antioxidant activities. E. oleracea was suggested to ease the oxidative stress and inflammation in brain cells. Our aim was to analyze the effects of E. oleracea on learning and memory. Seventy-two (250 ± 25 g) male Wistar albino rats were used for this study. The groups consisted of control, EO100 mg/kg, EO300 mg/kg, scopolamine 1.5 mg/kg, mecamylamine 7.5 mg/kg, combinations of scopolamine with EO100 mg/kg, EO300 mg/kg, and rivastigmine 1.5 mg/kg; and mecamylamine combined with EO100 mg/kg. Before the start of the study, E. oleracea doses were provided once a day for a period of 15 days and for a 6-day experimental period. Thirty minutes after intraperitoneal scopolamine and mecamylamine injections, gastrogavage was applied to each group. Ninety minutes after the drug treatments, locomotor activity and Morris water maze tests were performed. Rats were killed and each hippocampus was used for the quantification of acetylcholine (Ach). Statistical analyses were calculated using one-way and two-way analyses of variance (ANOVA), and a value of P < .05 was considered significant. In groups EO100 mg/kg and EO300 mg/kg the results did not show any significant changes on learning and memory compared with the control group. Mecamylamine and scopolamine enhanced the latency for the escape platform, and decreased the time spent in escape platform quadrant when the memory tests were applied in reference to the control value of P < .05. Scopolamine and mecamylamine combinations of EO100 mg/kg, EO300 mg/kg, and rivastigmine were proven to improve the memory. There was significant difference between the first and fifth days of the learning tests in all the groups, but no significant difference occurred between the groups. Ach levels in hippocampi supported all memory tests. We suggest that E. oleracea made no alterations on learning and memory, but still improved nicotinic and muscarinic receptor-mediated and impaired memory just as rivastigmine.
Keywords: Euterpe oleracea; Morris water maze; learning; rat; spatial memory.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Gasparini L, Racchi M, Binetti G, Trabucchi M, Solerte SB, Alkon D, Etcheberrigaray R, Gibson G, Blass J, Paoletti R, Govoni S: Peripheral markers in testing pathophysiological hypotheses and diagnosing Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J 1998;12:17–34 - PubMed
-
- Schauss AG, Wu X, Prior RL, et al. :. Phytochemical and nutrient composition of the freeze-dried Amazonian palm berry, Euterpe oleraceae Mart. (Acai). J Agricul Food Chem 2006;54:8598–8603 - PubMed
-
- Da Costa CA, Ognibene DT, Cordeiro VSC, de Bem GF, Santos IB, Soares RA, Resende AC: Effect of Euterpe oleracea Mart. seeds extract on chronic ischemic renal injury in renovascular hypertensive rats. J Med Food 2017;20:1002–1010 - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi KK, Pereira LF, Lamarão CV, Lima ES, da Veiga-Junior VF: Amazon acai: Chemistry and biological activities: A review. Food Chem 2015;179:137–151 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

