Progress Toward Rubella and Congenital Rubella Syndrome Control and Elimination - Worldwide, 2000-2018
- PMID: 31581161
- PMCID: PMC6776377
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6839a5
Progress Toward Rubella and Congenital Rubella Syndrome Control and Elimination - Worldwide, 2000-2018
Abstract
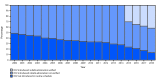
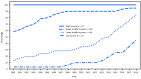
Rubella is a leading cause of vaccine-preventable birth defects. Although rubella virus infection usually causes a mild febrile rash illness in children and adults, infection during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, can result in miscarriage, fetal death, stillbirth, or a constellation of birth defects known as congenital rubella syndrome (CRS). A single dose of rubella-containing vaccine (RCV) can provide lifelong protection (1). In 2011, the World Health Organization (WHO) updated guidance on the use of RCV and recommended capitalizing on the accelerated measles elimination activities as an opportunity to introduce RCV (1). The Global Vaccine Action Plan 2011-2020 (GVAP) includes a target to achieve elimination of rubella in at least five of the six WHO regions by 2020 (2). This report on the progress toward rubella and CRS control and elimination updates the 2017 report (3), summarizing global progress toward the control and elimination of rubella and CRS from 2000 (the initiation of accelerated measles control activities) and 2012 (the initiation of accelerated rubella control activities) to 2018 (the most recent data) using WHO immunization and surveillance data. Among WHO Member States,* the number with RCV in their immunization schedules has increased from 99 (52% of 191) in 2000 to 168 (87% of 194) in 2018†; 69% of the world's infants were vaccinated against rubella in 2018. Rubella elimination has been verified in 81 (42%) countries. To make further progress to control and eliminate rubella, and to reduce the equity gap, introduction of RCV in all countries is important. Likewise, countries that have introduced RCV can achieve and maintain elimination with high vaccination coverage and surveillance for rubella and CRS. The two WHO regions that have not established an elimination goal (African [AFR] and Eastern Mediterranean [EMR]) should consider establishing a goal.§.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Rubella vaccines: WHO position paper. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2011;86:301–16. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global vaccine action plan. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2012. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/78141/9789241504980_eng...
-
- World Health Organization. Surveillance standards for vaccine-preventable diseases. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2018. https://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/burden/vpd/stan...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

