Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma in the Era of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
- PMID: 31581738
- PMCID: PMC6832444
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8101596
Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma in the Era of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
Abstract
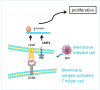
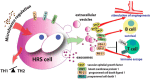
: The ligation of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) with programmed cell death ligand PD-L activates the immune checkpoint leading to T-cell dysfunction, exhaustion, and tolerance, especially in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) where the PD-L/ Janus kinase (Jak) signaling was frequently found altered. Anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies can reverse this immune checkpoint, releasing the brake on T-cell responses. The characterization of the mechanisms regulating both the expression of PD-1 and PD-L and their function(s) in HL is ongoing. We provide in this review the recent findings focused on this aim with special attention on the major research topics, such as adverse events and resistance to PD-1-PD-L1 inhibitor treatment, together with a part about angiogenesis, extracellular vesicles, and microbiome in HL pathogenesis.
Keywords: EBV; Hodgkin lymphoma; PD-1; PD-L1; adverse events; angiogenesis; cytokines; extracellular vesicles; immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Checkpoint Inhibitors Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2018 Dec;13(6):543-554. doi: 10.1007/s11899-018-0484-4. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2018. PMID: 30338457 Review.
-
Checkpoint Inhibition: Programmed Cell Death 1 and Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand Inhibitors in Hodgkin Lymphoma.Cancer J. 2016 Jan-Feb;22(1):17-22. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000164. Cancer J. 2016. PMID: 26841012 Review.
-
STAT3 Expression and Its Correlation with PD-L1 Expression in Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma and Hodgkin's Lymphoma at Dr. Saiful Anwar Regional Public Hospital in Malang, Indonesian Population.Adv Hematol. 2024 May 23;2024:7989996. doi: 10.1155/2024/7989996. eCollection 2024. Adv Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38817669 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for Recognizing and Managing Immune-Mediated Adverse Events in the Treatment of Hodgkin Lymphoma with Checkpoint Inhibitors.Oncologist. 2019 Jan;24(1):86-95. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0045. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30082490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Profiles and Biological Processes of Relapsed vs. Non-Relapsed Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 22;21(6):2185. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062185. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32235718 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes in Children, Adolescents, and Young-adults with Hodgkin's Lymphoma: a KPHOG Lymphoma Working-party, Multicenter, Retrospective Study.J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Nov 30;35(46):e393. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e393. J Korean Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33258329 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus BART microRNAs in EBV- associated Hodgkin lymphoma and gastric cancer.Infect Agent Cancer. 2020 Jun 23;15:42. doi: 10.1186/s13027-020-00307-6. eCollection 2020. Infect Agent Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32582365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-Immune Signatures of Treatment Resistance to Brentuximab Vedotin with Ipilimumab and/or Nivolumab in Hodgkin Lymphoma.Cancer Res Commun. 2024 Jul 1;4(7):1726-1737. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0252. Cancer Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38934093 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High PD-L1 Expression in HRS Cells and Macrophages in Tumor Immune Microenvironment Is Associated with Adverse Outcome and EBV Positivity in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 11;26(12):5592. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125592. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swerdlow S.H., Campo E., Pileri S.A., Harris N.L., Stein H., Siebert R., Advani R., Ghielmini M., Salles G.A., Zelenetz A.D., et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127:2375–2390. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

