New Frontiers in Diagnosis and Therapy of Circulating Tumor Markers in Cerebrospinal Fluid In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 31581745
- PMCID: PMC6830088
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8101195
New Frontiers in Diagnosis and Therapy of Circulating Tumor Markers in Cerebrospinal Fluid In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
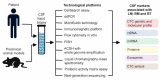
One of the greatest challenges in neuro-oncology is diagnosis and therapy (theranostics) of leptomeningeal metastasis (LM), brain metastasis (BM) and brain tumors (BT), which are associated with poor prognosis in patients. Retrospective analyses suggest that cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is one of the promising diagnostic targets because CSF passes through central nervous system, harvests tumor-related markers from brain tissue and, then, delivers them into peripheral parts of the human body where CSF can be sampled using minimally invasive and routine clinical procedure. However, limited sensitivity of the established clinical diagnostic cytology in vitro and MRI in vivo together with minimal therapeutic options do not provide patient care at early, potentially treatable, stages of LM, BM and BT. Novel technologies are in demand. This review outlines the advantages, limitations and clinical utility of emerging liquid biopsy in vitro and photoacoustic flow cytometry (PAFC) in vivo for assessment of CSF markers including circulating tumor cells (CTCs), circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), microRNA (miRNA), proteins, exosomes and emboli. The integration of in vitro and in vivo methods, PAFC-guided theranostics of single CTCs and targeted drug delivery are discussed as future perspectives.
Keywords: cerebrospinal liquid biopsy; circulating tumor cells; ctDNA; emboli; exosomes; in vivo flow cytometry; miRNA; targeted therapy; tumor biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Taillibert S., Chamberlain M.C. Leptomeningeal metastasis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018;149:169–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

