Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Stress Perfusion Imaging for Evaluation of Patients With Chest Pain
- PMID: 31582133
- PMCID: PMC8109181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.07.074
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Stress Perfusion Imaging for Evaluation of Patients With Chest Pain
Abstract
Background: Stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) has demonstrated excellent diagnostic and prognostic value in single-center studies.
Objectives: This study sought to investigate the prognostic value of stress CMR and downstream costs from subsequent cardiac testing in a retrospective multicenter study in the United States.
Methods: In this retrospective study, consecutive patients from 13 centers across 11 states who presented with a chest pain syndrome and were referred for stress CMR were followed for a target period of 4 years. The authors associated CMR findings with a primary outcome of cardiovascular death or nonfatal myocardial infarction using competing risk-adjusted regression models and downstream costs of ischemia testing using published Medicare national payment rates.
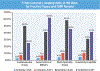
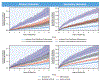
Results: In this study, 2,349 patients (63 ± 11 years of age, 47% female) were followed for a median of 5.4 years. Patients with no ischemia or late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) by CMR, observed in 1,583 patients (67%), experienced low annualized rates of primary outcome (<1%) and coronary revascularization (1% to 3%), across all years of study follow-up. In contrast, patients with ischemia+/LGE+ experienced a >4-fold higher annual primary outcome rate and a >10-fold higher rate of coronary revascularization during the first year after CMR. Patients with ischemia and LGE both negative had low average annual cost spent on ischemia testing across all years of follow-up, and this pattern was similar across the 4 practice environments of the participating centers.
Conclusions: In a multicenter U.S. cohort with stable chest pain syndromes, stress CMR performed at experienced centers offers effective cardiac prognostication. Patients without CMR ischemia or LGE experienced a low incidence of cardiac events, little need for coronary revascularization, and low spending on subsequent ischemia testing. (Stress CMR Perfusion Imaging in the United States [SPINS]: A Society for Cardiovascular Resonance Registry Study; NCT03192891).
Keywords: cost of care; prognosis; stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




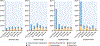
Comment in
-
The SPINS Trial: Building Evidence and a Consequence?J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Oct 8;74(14):1756-1759. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.07.075. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31582134 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schwitter J, Wacker CM, Wilke N, et al. for the MR-IMPACT Investigators. MR-IMPACT II: Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Myocardial Perfusion Assessment in Coronary artery disease Trial: perfusion-cardiac magnetic resonance vs. single-photon emission computed tomography for the detection of coronary artery disease: a comparative multicentre, multivendor trial. Eur Heart J 2013;34:775–81. - PubMed
-
- Schwitter J, Wacker CM, Wilke N, et al. for the MR-IMPACT Investigators. Superior diagnostic performance of perfusion-cardiovascular magnetic resonance versus SPECT to detect coronary artery disease: the secondary endpoints of the multicenter multivendor MR-IMPACT II (Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Myocardial Perfusion Assessment in Coronary Artery Disease Trial). J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2012;14:61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schwitter J, Wacker CM, van Rossum AC, et al. MR-IMPACT: comparison of perfusion-cardiac magnetic resonance with single-photon emission computed tomography for the detection of coronary artery disease in a multicentre, multivendor, randomized trial. Eur Heart J 2008;29:480–9. - PubMed
-
- Watkins S, McGeoch R, Lyne J, et al. Validation of magnetic resonance myocardial perfusion imaging with fractional flow reserve for the detection of significant coronary heart disease. Circulation 2009;120:2207–13. - PubMed
-
- Bodi V, Sanchis J, Lopez-Lereu MP, et al. Prognostic value of dipyridamole stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;50:1174–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

