A new era for giant cell arteritis
- PMID: 31582795
- PMCID: PMC7253415
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-019-0608-7
A new era for giant cell arteritis
Abstract
The landscape of the investigation and management of giant cell arteritis (GCA) is advancing. In this review we will outline the recent advances by searching the current English literature for relevant articles using key words of giant cell arteritis, temporal arteritis, Horton's disease, investigation, and treatment. Delay in diagnosis, diagnostic uncertainty and glucocorticoid (GC) morbidity are among the highest concerns of clinicians and patients in this disease area. The positive news is that fast track pathways, imaging techniques and new therapies are emerging for routine management of GCA. Future directions for intervention in the treatment paradigm will be discussed.
摘要: 巨细胞动脉炎 (GCA) 的诊疗发生了很大进展。在这篇综述中, 我们通过关键词搜索目前相关的英文文献, 以总结和回顾巨细胞动脉炎的最新进展。所使用的关键词为巨细胞动脉炎; 颞动脉炎; 霍顿病;观察;治疗等。在GCA疾病领域内, 临床医生和患者们最关注的问题是诊断延迟, 诊断不确定性和糖皮质激素 (GC) 的使用情况。好消息是诊疗快速通道的建立, 成像技术以及新治疗的日新月异已经应用于GCA的常规管理。在本文中我们也会探讨治疗、干预策略的新方向。.
Conflict of interest statement
SPM has undertaken consultancy work (speaker and advisory board fees) from Roche. VQ has undertaken consultancy work (speaker and advisory board fees) for Roche. Other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




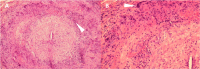


Comment in
-
Response to 'Comment on: 'A new era for giant cell arteritis''.Eye (Lond). 2020 Oct;34(10):1929-1930. doi: 10.1038/s41433-019-0703-9. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Eye (Lond). 2020. PMID: 31767962 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comment on: 'A new era for giant cell arteritis'.Eye (Lond). 2020 Oct;34(10):1927-1928. doi: 10.1038/s41433-019-0701-y. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Eye (Lond). 2020. PMID: 31767963 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Buttgereit F, Dejaco C, Matteson E, Dasgupta B. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: a systematic review. JAMA. 2016;315:2442–58. - PubMed
-
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Medium- and large-vessel vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:160–9. - PubMed
-
- Dejaco C, Duftner C, Buttgereit F, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. The spectrum of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: revisiting the concept of the disease. Rheumatology. 2017;56:506–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

