Patterns of phlebotomy blood loss and transfusions in extremely low birth weight infants
- PMID: 31582812
- PMCID: PMC7331095
- DOI: 10.1038/s41372-019-0515-6
Patterns of phlebotomy blood loss and transfusions in extremely low birth weight infants
Abstract
Objective: Characterize frequency and volume of blood draws and transfusions in extremely low birth weight infants in the first 10 weeks of life.
Study design: We included infants with a birth weight <1000 g born 23 0/7-29 6/7 weeks gestational age (GA) and with a length of stay ≥10 weeks, admitted between 2014 and 2016 to a single neonatal intensive care unit.
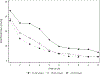
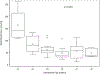
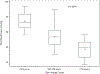
Results: Of 54 infants, median (25th, 75th percentile) GA and birth weight were 25 weeks (24, 26) and 665 g (587, 822), respectively. Median number of blood draws per infant decreased from 57 (49, 65) in week 1 to 12 (8, 22) in week 10. Median volume of blood extracted was 83 mL (70, 97), and median number of blood transfusions was 8 (5, 10).
Conclusions: This cohort experienced a high number and volume of blood draws. Draw frequency and transfusions decreased over the first 10 weeks of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards
Figures
References
-
- Colombatti R, Sainati L, Trevisanuto D. Anemia and transfusion in the neonate. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;21:2–9. - PubMed
-
- Juul S Erythropoiesis and the approach to anemia in premature infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25:97–9. - PubMed
-
- Ringer SA, Richardson DK, Sacher RA, Keszler M, Churchill WH. Variations in transfusion practice in neonatal intensive care. Pediatrics. 1998;101:194–200. - PubMed
-
- Obladen M, Sachsenweger M, Stahnke M. Blood sampling in very low birth weight infants receiving different levels of intensive care. Eur J Pediatr. 1988;147:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Madan A, Kumar R, Adams MM, Benitz WE, Geaghan SM, Widness JA. Reduction in red blood cell transfusions using a bedside analyzer in extremely low birth weight infants. J Perinatol. 2005;25:21–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

