Histone lysine methyltransferases in biology and disease
- PMID: 31582846
- PMCID: PMC6951022
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-019-0298-7
Histone lysine methyltransferases in biology and disease
Abstract
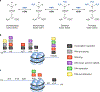
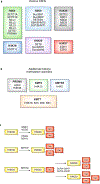
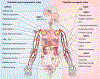
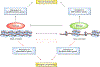
The precise temporal and spatial coordination of histone lysine methylation dynamics across the epigenome regulates virtually all DNA-templated processes. A large number of histone lysine methyltransferase (KMT) enzymes catalyze the various lysine methylation events decorating the core histone proteins. Mutations, genetic translocations and altered gene expression involving these KMTs are frequently observed in cancer, developmental disorders and other pathologies. Therapeutic compounds targeting specific KMTs are currently being tested in the clinic, although overall drug discovery in the field is relatively underdeveloped. Here we review the biochemical and biological activities of histone KMTs and their connections to human diseases, focusing on cancer. We also discuss the scientific and clinical challenges and opportunities in studying KMTs.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
O.G. is a cofounder of Epicypher, Inc., and Athelas Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

