Long-Term Outcome in Patients with a Solitary Peutz-Jeghers Polyp
- PMID: 31582972
- PMCID: PMC6754916
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8159072
Long-Term Outcome in Patients with a Solitary Peutz-Jeghers Polyp
Abstract
Background: Clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with a solitary Peutz-Jeghers polyp (PJP) have not been fully investigated.
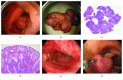
Methods: Solitary PJP was diagnosed when a single hamartomatous lesion was identified in the gastrointestinal tract of patients without mucocutaneous pigmentation or a family history of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. We retrospectively reviewed 51 patients (32 men and 19 women) with a solitary PJP and analyzed the sex, age at diagnosis, endoscopic features, and outcomes in this patient group. The STK11/LKB1 germline mutation was not investigated in any of the patients.
Results: The mean age of the 51 patients was 66.1 years. The polyp was found in the duodenum (N = 10), jejunum (N = 2), cecum (N = 2), transverse colon (N = 5), sigmoid colon (N = 21), or rectum (N = 11). Most of the polyps presented as a pedunculated lesion (N = 40), followed by semipedunculated (N = 9) and sessile (N = 2) morphologies. The mean size of a solitary PJP was 15.6 mm (range: 5 to 33 mm). During a mean endoscopic follow-up period of 4.5 years (range: 0.1 to 16.1 years), no recurrence was identified. Eighteen of the enrolled patients had a history of cancer or concomitant cancer. Five patients died due to non-gastrointestinal-related causes. No additional cancer or death directly related to solitary PJP was observed.
Conclusions: Solitary PJPs did not recur in this study. Although examination of the entire gastrointestinal tract using esophagogastroduodenoscopy, enteroscopy, and colonoscopy is desirable to exclude Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, follow-up endoscopy after endoscopic polyp resection may be unnecessary, once the diagnosis of a solitary PJP is made.
Copyright © 2019 Masaya Iwamuro et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

