Oncotype DX recurrence score implications for disparities in chemotherapy and breast cancer mortality in Georgia
- PMID: 31583272
- PMCID: PMC6763428
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-019-0129-3
Oncotype DX recurrence score implications for disparities in chemotherapy and breast cancer mortality in Georgia
Abstract
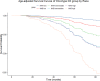
Among women diagnosed with stage I-IIIa, node-negative, hormone receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer (BC), Oncotype DX recurrence scores (ODX RS) inform chemotherapy treatment decisions. Differences in recurrence scores or testing may contribute to racial disparities in BC mortality among women with HR+ tumors. We identified 12,081 non-Hispanic White (NHW) and non-Hispanic Black (NHB) BC patients in Georgia (2010-2014), eligible to receive an ODX RS. Logistic regression was used to estimate the odds of chemotherapy receipt by race and ODX RS. Cox proportional hazard regression was used to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) comparing BC mortality rates by race and recurrence score. Receipt of Oncotype testing was consistent between NHB and NHW women. Receipt of chemotherapy was generally comparable within strata of ODX RS-although NHB women with low scores were slightly more likely to receive chemotherapy (OR = 1.16, 95% CI 0.77, 1.75), and NHB women with high scores less likely to receive chemotherapy (OR = 0.77, 95% CI 0.48, 1.24), than NHW counterparts. NHB women with a low recurrence score had the largest hazard of BC mortality (HR = 2.47 95% CI 1.22, 4.99) compared to NHW women. Our data suggest that additional tumor heterogeneity, or other downstream treatment factors, not captured by ODX, may be drivers of racial disparities in HR+ BC.
Keywords: Predictive markers; Prognostic markers.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsK.G. is on the advisory board with Pfizer and Lilly and has received research funding from Pfizer, Calithera, and Merck. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Blok EJ, et al. Systematic review of the clinical and economic value of gene expression profiles for invasive early breast cancer available in Europe. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018;62:74–90. - PubMed
-
- Reis-Filho JS, Pusztai L. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: classification, prognostication, and prediction. Lancet (Lond., Engl.) 2011;378:1812–1823. - PubMed
-
- Gradishar WJ, et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Breast Cancer, Version 1.2017. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw.: JNCCN. 2017;15:433–451. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

