Catalytic Cycle of Neisseria meningitidis CMP-Sialic Acid Synthetase Illustrated by High-Resolution Protein Crystallography
- PMID: 31583886
- PMCID: PMC7814854
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00517
Catalytic Cycle of Neisseria meningitidis CMP-Sialic Acid Synthetase Illustrated by High-Resolution Protein Crystallography
Abstract
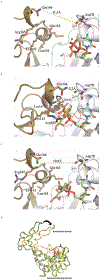
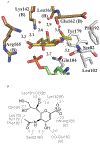
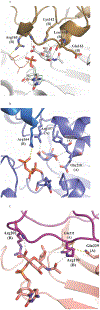
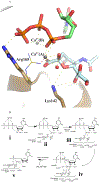
Cytidine 5'-monophosphate (CMP)-sialic acid synthetase (CSS) is an essential enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates containing sialic acids, a class of α-keto acids that are generally terminal key recognition residues by many proteins that play important biological and pathological roles. The CSS from Neisseria meningitidis (NmCSS) has been commonly used with other enzymes such as sialic acid aldolase and/or sialyltransferase in synthesizing a diverse array of compounds containing sialic acid or its naturally occurring and non-natural derivatives. To better understand its catalytic mechanism and substrate promiscuity, four NmCSS crystal structures trapped at various stages of the catalytic cycle with bound substrates, substrate analogues, and products have been obtained and are presented here. These structures suggest a mechanism for an "open" and "closed" conformational transition that occurs as sialic acid binds to the NmCSS/cytidine-5'-triphosphate (CTP) complex. The closed conformation positions critical residues to help facilitate the nucleophilic attack of sialic acid C2-OH to the α-phosphate of CTP, which is also aided by two observed divalent cations. Product formation drives the active site opening, promoting the release of products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
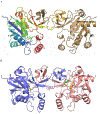
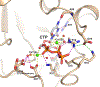
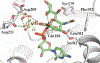
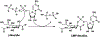
Similar articles
-
Pasteurella multocida CMP-sialic acid synthetase and mutants of Neisseria meningitidis CMP-sialic acid synthetase with improved substrate promiscuity.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Mar;93(6):2411-23. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3579-6. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 21968653
-
Identification and characterization of important residues in the catalytic mechanism of CMP-Neu5Ac synthetase from Neisseria meningitidis.FEBS J. 2010 Jul;277(13):2779-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07696.x. Epub 2010 May 20. FEBS J. 2010. PMID: 20491913 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of CMP-N-acetylneuraminate synthetase from Vibrio cholerae.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2019 Jun 1;75(Pt 6):564-577. doi: 10.1107/S2059798319006831. Epub 2019 May 31. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 31205019 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial CMP-sialic acid synthetases: production, properties, and applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008 Oct;80(5):757-65. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1643-7. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18716769 Review.
-
CMP-Sialic Acid Synthetase: The Point of Constriction in the Sialylation Pathway.Top Curr Chem. 2015;366:139-67. doi: 10.1007/128_2013_477. Top Curr Chem. 2015. PMID: 24141690 Review.
Cited by
-
The Lst Sialyltransferase of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Can Transfer Keto-Deoxyoctanoate as the Terminal Sugar of Lipooligosaccharide: a Glyco-Achilles Heel That Provides a New Strategy for Vaccines to Prevent Gonorrhea.mBio. 2021 Mar 23;12(2):e03666-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03666-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33758087 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Role of Sialylation in Cancer Metastasis, Immunity, and Therapeutic Opportunity.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 26;14(23):5840. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235840. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Many locks to one key: N-acetylneuraminic acid binding to proteins.IUCrJ. 2024 Sep 1;11(Pt 5):664-674. doi: 10.1107/S2052252524005360. IUCrJ. 2024. PMID: 38965900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enabling Chemoenzymatic Strategies and Enzymes for Synthesizing Sialyl Glycans and Sialyl Glycoconjugates.Acc Chem Res. 2024 Jan 16;57(2):234-246. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00614. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38127793 Free PMC article.
-
L. pneumophila CMP-5,7-di-N-acetyllegionaminic acid synthetase (LpCLS)-involved chemoenzymatic synthesis of sialosides and analogues.Org Biomol Chem. 2020 Jan 28;18(4):738-744. doi: 10.1039/c9ob02476j. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Org Biomol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31912849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sellmeier M, Weinhold B, and Munster-Kuhnel A (2013) CMP-Sialic Acid Synthetase: The Point of Constriction in the Sialylation Pathway. Top. Curr. Chem 366, 139–167. - PubMed
-
- Mizanur RM, and Pohl NL (2008) Bacterial CMP-sialic acid synthetases: production, properties, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 80, 757–765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

