Segregation of the mouse germline and soma
- PMID: 31583942
- PMCID: PMC6816410
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1672466
Segregation of the mouse germline and soma
Abstract
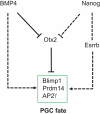
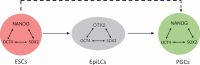
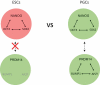
Mouse primordial germ cells (PGCs), originate from the early post-implantation epiblast in response to BMP4 secreted by the extraembryonic ectoderm. However, how BMP4 acts here has remained unclear. Recent work has identified the transcription factor (TF), OTX2 as a key determinant of the segregation of the germline from the soma. OTX2 is expressed ubiquitously in the early post-implantation epiblast, decreasing rapidly in cells that initiate the PGC programme. Otx2 mRNA is also rapidly repressed by BMP4 in vitro, in germline competent cells. Supporting a model in which BMP4 represses Otx2, enforcing sustained OTX2 expression in competent cells blocks germline entry. In contrast, Otx2-null epiblast cells enter the germline with increased efficiency in vitro and in vivo and can do so independently of BMP4. Also, Otx2-null cells can initiate germline entry even without the crucial PGC TF, BLIMP1. In this review, we survey recent advances and propose hypotheses concerning germline entry.
Keywords: NANOG; OTX2; Primordial germ cell; formative pluripotency; germline competent; transcription factors.
Figures

References
-
- Ohinata Y, Ohta H, Shigeta M, et al. A signaling principle for the specification of the germ cell lineage in mice. Cell. 2009;137:571–584. - PubMed
-
- Saitou M, Barton SC, Surani MA.. A molecular programme for the specification of germ cell fate in mice. Nature. 2002;418:293–300. - PubMed
-
- Ohinata Y, Payer B, O’Carroll D, et al. Blimp1 is a critical determinant of the germ cell lineage in mice. Nature. 2005;436:207–213. - PubMed
-
- Yamaji M, Seki Y, Kurimoto K, et al. Critical function of Prdm14 for the establishment of the germ cell lineage in mice. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1016–1022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
