Estimating population immunity to poliovirus in Jordan's high-risk areas
- PMID: 31584319
- PMCID: PMC7227716
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1667727
Estimating population immunity to poliovirus in Jordan's high-risk areas
Abstract
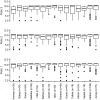
A community-based serosurvey was conducted among children ages 6-59 to assess population immunity in Jordan's high-risk areas following the Middle East polio outbreak response. The survey was a two-stage cluster-quota sample with high risk areas as the primary sampling units. High-risk areas included border and hard-to-reach areas, and areas with a high proportion of refugees, mobile communities and/or low coverage during previous immunization campaigns. Population immunity to poliovirus was high overall. In high-risk areas, Type 1 seroprevalence = 98% (95% CI = 96, 99), Type 2 = 98% (95% CI = 96, 99) and Type 3 = 96% (95% CI = 94, 98). Seroprevalence was higher in the refugee camps: Type 1 seroprevalence = 99.6% (95% CI = 97.9, 100); Type 2: 99.6% (95% CI = 97.9, 99.9), and Type 3: 100% (95% CI = 100,100). The vigilance that the Jordan Ministry of Health has placed on locating and vaccinating high-risk populations has been successful in maintaining high population immunity and averting polio outbreaks despite the influx of refugees from Syria.
Keywords: Jordan; Poliovirus; immunization strategy; oral polio vaccine; seroprevalence.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . [accessed 2017 June13]. http://polioeradication.org/tools-and-library/policy-reports/declaration....
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Tracking progress toward global polio eradication, 2010–2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2012;61:265–69. - PubMed
-
- Sixty Fifth World Health Assembly . [accessed 2017 June13]. http://polioeradication.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/A65_R5-en.pdf.
-
- Weldon WC, Oberste MS, Pallansch MA.. Standardized methods for detection of poliovirus antibodies. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1387:145–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
