Using community-based system dynamics modeling to understand the complex systems that influence health in cities: The SALURBAL study
- PMID: 31586769
- PMCID: PMC6919340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2019.102215
Using community-based system dynamics modeling to understand the complex systems that influence health in cities: The SALURBAL study
Abstract
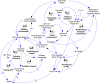
We discuss the design, implementation, and results of a collaborative process designed to elucidate the complex systems that drive food behaviors, transport, and health in Latin American cities and to build capacity for systems thinking and community-based system dynamics (CBSD) methods among diverse research team members and stakeholders. During three CBSD workshops, 62 stakeholders from 10 Latin American countries identified 98 variables and a series of feedback loops that shape food behaviors, transportation and health, along with 52 policy levers. Our findings suggest that CBSD can engage local stakeholders, help them view problems through the lens of complex systems and use their insights to prioritize research efforts and identify novel solutions that consider mechanisms of complexity.
Keywords: Community-based system dynamics; Diet; Group model building; Latin America; Transport.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen D.F., Richardson G.P., Vennix J.A. Group model building: adding more science to the craft. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1997;13:187–201.
-
- Bai X., Nath I., Capon A., Hasan N., Jaron D. Health and wellbeing in the changing urban environment: complex challenges, scientific responses, and the way forward. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2012;4:465–472.
-
- Beran D., Chappuis F., Damasceno A., Jha N., Pesantes M.A., Singh S.B., Somerville C., Suggs L.S., Miranda J.J. High-quality health systems: time for a revolution in research and research funding. The. Lancet. Glob. Health. 2019;7:e303–e304. - PubMed
-
- Black L.J., Andersen D.F. Using visual representations as boundary objects to resolve conflict in collaborative model-building approaches. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2012;29:194–208.
-
- Bopp M., Kaczynski A.T., Campbell M.E. Social ecological influences on work-related active commuting among adults. Am. J. Health Behav. 2013;37:543–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

