High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin and the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 31587565
- PMCID: PMC6970546
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042960
High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin and the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: The introduction of more sensitive cardiac troponin assays has led to increased recognition of myocardial injury in acute illnesses other than acute coronary syndrome. The Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction recommends high-sensitivity cardiac troponin testing and classification of patients with myocardial injury based on pathogenesis, but the clinical implications of implementing this guideline are not well understood.
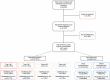
Methods: In a stepped-wedge cluster randomized, controlled trial, we implemented a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assay and the recommendations of the Universal Definition in 48 282 consecutive patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome. In a prespecified secondary analysis, we compared the primary outcome of myocardial infarction or cardiovascular death and secondary outcome of noncardiovascular death at 1 year across diagnostic categories.
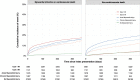
Results: Implementation increased the diagnosis of type 1 myocardial infarction by 11% (510/4471), type 2 myocardial infarction by 22% (205/916), and acute and chronic myocardial injury by 36% (443/1233) and 43% (389/898), respectively. Compared with those without myocardial injury, the rate of the primary outcome was highest in those with type 1 myocardial infarction (cause-specific hazard ratio [HR] 5.64 [95% CI, 5.12-6.22]), but was similar across diagnostic categories, whereas noncardiovascular deaths were highest in those with acute myocardial injury (cause specific HR 2.65 [95% CI, 2.33-3.01]). Despite modest increases in antiplatelet therapy and coronary revascularization after implementation in patients with type 1 myocardial infarction, the primary outcome was unchanged (cause specific HR 1.00 [95% CI, 0.82-1.21]). Increased recognition of type 2 myocardial infarction and myocardial injury did not lead to changes in investigation, treatment or outcomes.
Conclusions: Implementation of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays and the recommendations of the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction identified patients at high-risk of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular events but was not associated with consistent increases in treatment or improved outcomes. Trials of secondary prevention are urgently required to determine whether this risk is modifiable in patients without type 1 myocardial infarction.
Clinical trial registration: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01852123.
Keywords: myocardial infarction; troponin.
Figures


Comment in
-
The Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction and the Emerging Importance of Myocardial Injury.Circulation. 2020 Jan 21;141(3):172-175. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044125. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 31958242 No abstract available.
-
Response by Wereski et al to Letter Regarding Article, "High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin and the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction".Circulation. 2020 Jun 9;141(23):e882-e883. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047269. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32511002 No abstract available.
-
Letter by Coscia et al Regarding Article, "High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin and the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction".Circulation. 2020 Jun 9;141(23):e880-e881. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.046527. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32511004 No abstract available.
References
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons ML, Chaitman BR, White HD, Katus HA, Apple FS, Lindahl B, Morrow DA, et al. Writing Group on the Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG) Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2551–2567. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs184.
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Chaitman BR, Bax JJ, Morrow DA, White HD ESC Scientific Document Group. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Eur Heart J. 2019;40:237–269. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy462. - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, Jaffe AS, Apple FS, Galvani M, Katus HA, Newby LK, Ravkilde J, Chaitman B, et al. Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Redefinition of Myocardial Infarction. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2007;116:2634–2653. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187397. - PubMed
-
- Apple FS, Collinson PO IFCC Task Force on Clinical Applications of Cardiac Biomarkers. Analytical characteristics of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays. Clin Chem. 2012;58:54–61. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2011.165795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- FS/19/17/34172/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/16/14/32023/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/18/25/33454/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- SP/18/2/33800/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/16/75/32533/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CH/09/002/26360/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RE/18/6/3421/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- SP/12/10/29922/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RE/18/5/34216/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- BCDSA/100003/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CH/09/002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

