pH-Responsive Carboxymethylcellulose Nanoparticles for 68Ga-WBC Labeling in PET Imaging
- PMID: 31590371
- PMCID: PMC6835547
- DOI: 10.3390/polym11101615
pH-Responsive Carboxymethylcellulose Nanoparticles for 68Ga-WBC Labeling in PET Imaging
Abstract
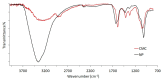
Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) is a well-known pharmaceutical polymer, recently gaining attention in the field of nanomedicine, especially as a polyelectrolyte agent for the formation of complexes with oppositely charged macromolecules. Here, we report on the application of pH-sensitive pharmaceutical grade CMC-based nanoparticles (NP) for white blood cells (WBC) PET imaging. In this context and as an alternative to 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT labeling, the use of 68Ga3+ as PET radionuclide was investigated since, at early time points, it could provide the greater spatial resolution and patient convenience of PET tomography over SPECT clinical practices. Two operator-friendly kit-type formulations were compared, with the intention of radiolabeling within a short time (10 min), under mild conditions (physiological pH, room temperature) and in agreement with the actual clinically applied guidelines. NP were labeled by directly using 68Ga3+ eluted in HCL 0.05 N, from hospital suited 68Ge/68Ga generator and in absence of chelator. The first kit type approach involved the application of 68Ga3+ as an ionotropic gelation agent for in-situ forming NP. The second kit type approach concerned the re-hydration of a proper freeze-dried injectable NP powder. pH-sensitive NP with 250 nm average diameter and 80% labeling efficacy were obtained. The NP dispersant medium, including a cryoprotective agent, was modulated in order to optimize the Zeta potential value (-18 mV), minimize the NP interaction with serum proteins and guarantee a physiological environment for WBC during NP incubation. Time-dependent WBC radiolabeling was correlated to NP uptake by using both confocal and FT-IR microscopies. The ready to use lyophilized NP formulation approach appears promising as a straightforward 68Ga-WBC labeling tool for PET imaging applications.
Keywords: 68Ga; PET; WBC labeling; carboxymethylcellulose; nanoparticles; pH sensitive; radiolabeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
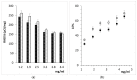
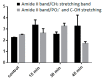
 ) and 15 min (
) and 15 min ( ), (b) LE% after 5 min (■) or 15 min (□).
), (b) LE% after 5 min (■) or 15 min (□).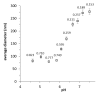
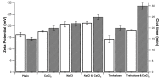
 ). All samples contained CMC-based NP (5 mg/mL) in 0.1 M Tris-buffered at pH 7.4 (Plain), then, salts and cryo-protector agent were added either alone or combined: CaCl2 (0.4 mM), NaCl (0.9%), and Trehalose (5%).
). All samples contained CMC-based NP (5 mg/mL) in 0.1 M Tris-buffered at pH 7.4 (Plain), then, salts and cryo-protector agent were added either alone or combined: CaCl2 (0.4 mM), NaCl (0.9%), and Trehalose (5%).

References
-
- Chiappe C., Rodriguez Douton M.J., Mezzetta A., Guazzelli L., Pomelli C.S., Assanelli G., de Angelis A.R. Exploring and exploiting different catalytic systems for the direct conversion of cellulose into levulinic acid. New J. Chem. 2018;42:1845–1852. doi: 10.1039/C7NJ04707J. - DOI
-
- Pettignano A., Charlot A., Fleury E. Carboxyl-functionalized derivatives of carboxymethyl cellulose: Towards advanced biomedical applications. Polym. Rev. 2019;59:510–560. doi: 10.1080/15583724.2019.1579226. - DOI
-
- Carvalho S.M., Leonel A.G., Mansur A.A.P., Carvalho I.C., Krambrock K., Mansur H.S. Bifunctional magnetopolymersomes of iron oxide nanoparticles and carboxymethylcellulose conjugated with doxorubicin for hyperthermo-chemotherapy of brain cancer cells. Biomater. Sci. 2019;7:2102–2122. doi: 10.1039/C8BM01528G. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

