Migration Studies of Two Common Components of UV-curing Inks into Food Simulants
- PMID: 31591310
- PMCID: PMC6804053
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24193607
Migration Studies of Two Common Components of UV-curing Inks into Food Simulants
Abstract
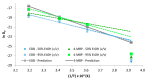
The Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) has reported many cases of different UV curing inks components in foodstuffs during the last few years. These contaminants reach foodstuffs mainly by set-off, their principal migration mechanism from the package. Under this premise, this work has tried to characterize the process of migration of two common UV ink components: a photoinitiator (4-Methylbenzophenone) and a coinitiator (Ethyl-4-(dimethylamino) benzoate), from the most common plastic material used in food packaging low-density polyethylene (LDPE) into six different food simulants. The migration kinetics tests were performed at four different common storage temperatures, obtaining the key migration parameters for both molecules: the coefficients of diffusion and partition. The migration process was highly dependent on the storage conditions, the photoinitiator properties and the pH of the foodstuff.
Keywords: 4-methylbenzophenone; diffusion coefficient; ethyl-4-(dimethylamino) benzoate; migration; partition coefficient.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Castle L., Bradley E.L. Residues of food contact materials. In: Nollet L.N.L., Toldrá F., editors. Handbook of Dairy Foods Analysis. 1st ed. Taylor & Francis; Boca Ratón, FL, USA: 2010. pp. 755–775.
-
- Simoneau C. Food contact materials. In: Picó Y., editor. Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry. Food Contaminants and Residue Analysis. 1st ed. Volume 51. Elsevier; Oxford, UK: 2008. pp. 733–774.
-
- Helmroth I.E., Rijk R., Dekker M., Jongen W. Predictive modelling of migration from packaging materials into food products for regulatory purposes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002;13:102–109. doi: 10.1016/S0924-2244(02)00031-6. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

