An atlas of cortical circular RNA expression in Alzheimer disease brains demonstrates clinical and pathological associations
- PMID: 31591557
- PMCID: PMC6858549
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-019-0501-5
An atlas of cortical circular RNA expression in Alzheimer disease brains demonstrates clinical and pathological associations
Abstract
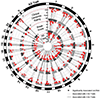
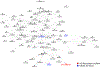
Parietal cortex RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data were generated from individuals with and without Alzheimer disease (AD; ncontrol = 13; nAD = 83) from the Knight Alzheimer Disease Research Center (Knight ADRC). Using this and an independent (Mount Sinai Brain Bank (MSBB)) AD RNA-seq dataset, cortical circular RNA (circRNA) expression was quantified in the context of AD. Significant associations were identified between circRNA expression and AD diagnosis, clinical dementia severity and neuropathological severity. It was demonstrated that most circRNA-AD associations are independent of changes in cognate linear messenger RNA expression or estimated brain cell-type proportions. Evidence was provided for circRNA expression changes occurring early in presymptomatic AD and in autosomal dominant AD. It was also observed that AD-associated circRNAs co-expressed with known AD genes. Finally, potential microRNA-binding sites were identified in AD-associated circRNAs for miRNAs predicted to target AD genes. Together, these results highlight the importance of analyzing non-linear RNAs and support future studies exploring the potential roles of circRNAs in AD pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

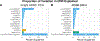
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG046374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG044546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057777/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG071706/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058922/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG044546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052411/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG053303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG058501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG049087/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG064877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

