The Gastroenterologist's Guide to Preventive Management of Compensated Cirrhosis
- PMID: 31592079
- PMCID: PMC6771034
The Gastroenterologist's Guide to Preventive Management of Compensated Cirrhosis
Abstract
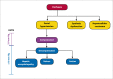
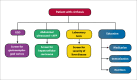
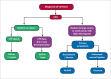
Despite advances in medical care, the prevalence and mortality associated with cirrhosis continue to rise. The majority of medical care and physician efforts are devoted to the management of decompensated cirrhosis and its complications of gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hepatic encephalopathy, and ascites; however, limited efforts are placed on the medical management of compensated cirrhosis. Patients with compensated cirrhosis carry a higher survival rate, and, when diagnosed early, may be screened for future decompensation. When possible, these patients can be treated for their underlying disease to prevent disease progression and avoid the need for liver transplantation. This article reviews the importance of early diagnosis, outpatient management of compensated cirrhosis, early screening for potential decompensation, and patient education.
Keywords: Compensated cirrhosis; gastroesophageal varices; hepatocellular carcinoma; malnutrition; patient education; polypharmacy.
Copyright © 2019, Gastro-Hep Communications, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2016. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2018;67(6):1–77. - PubMed
-
- Allen AM, Kim WR, Moriarty JP, Shah ND, Larson JJ, Kamath PS. Time trends in the health care burden and mortality of acute on chronic liver failure in the United States. Hepatology. 2016;64(6):2165–2172. - PubMed
-
- Rinella ME, Sanyal AJ. Management of NAFLD: a stage-based approach. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(4):196–205. - PubMed
-
- Lin ZH, Xin YN, Dong QJ, et al. Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: an updated meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011;53(3):726–736. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
