Integrative Molecular Analysis of Patients With Advanced and Metastatic Cancer
- PMID: 31592503
- PMCID: PMC6778956
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.19.00047
Integrative Molecular Analysis of Patients With Advanced and Metastatic Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: We developed a precision medicine program for patients with advanced cancer using integrative whole-exome sequencing and transcriptome analysis.
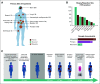
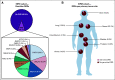
Patients and methods: Five hundred fifteen patients with locally advanced/metastatic solid tumors were prospectively enrolled, and paired tumor/normal sequencing was performed. Seven hundred fifty-nine tumors from 515 patients were evaluated.
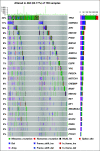
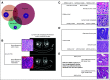
Results: Most frequent tumor types were prostate (19.4%), brain (16.5%), bladder (15.4%), and kidney cancer (9.2%). Most frequently altered genes were TP53 (33%), CDKN2A (11%), APC (10%), KTM2D (8%), PTEN (8%), and BRCA2 (8%). Pathogenic germline alterations were present in 10.7% of patients, most frequently CHEK2 (1.9%), BRCA1 (1.5%), BRCA2 (1.5%), and MSH6 (1.4%). Novel gene fusions were identified, including a RBM47-CDK12 fusion in a metastatic prostate cancer sample. The rate of clinically relevant alterations was 39% by whole-exome sequencing, which was improved by 16% by adding RNA sequencing. In patients with more than one sequenced tumor sample (n = 146), 84.62% of actionable mutations were concordant.
Conclusion: Integrative analysis may uncover informative alterations for an advanced pan-cancer patient population. These alterations are consistent in spatially and temporally heterogeneous samples.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHORS’ DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO’s conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/po/author-center. Alexandros Sigaras Employment: Weill Cornell Medical College Loredana Puca Employment: Petra Pharma Corporation Bishoy M. Faltas Honoraria: Digital Science Press publications Research Funding: Eli Lilly David Rickman Research Funding: Janssen Oncology Eleni Andreopoulou Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Sirtex, SVB Leerink, AbbVie, Eisai, NanoString Technologies Consulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, Sirtex, SVB Leerink, AbbVie, Eisai, NanoString Technologies Speakers’ Bureau: R-Pharm US Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: AstraZeneca, Sirtex, SVB Leerink, AbbVie, Eisai, NanoString Technologies Kevin Holcomb Research Funding: Fujirebio Diagnostics Expert Testimony: Johnson & Johnson Linda T. Vahdat Honoraria: Polyphor, R-Pharm, Athenex, Seattle Genetics, Osmol Therapeutics Consulting or Advisory Role: Berg Pharma Speakers’ Bureau: Eisai Research Funding: Polyphor (Inst), Immunomedics (Inst), Seattle Genetics (Inst) Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Patent pending on the application for BMD progenitor cells (Inst) Douglas S. Scherr Research Funding: Urogen Pharma (Inst), Cepheid (Inst), Anchiano (Inst), CryoLife (Inst) Koen van Besien Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Hemogenyx Consulting or Advisory Role: Hemogenyx, Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Cellectis, Tessa Therapeutics Research Funding: Miltenyi Biotec, Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Juno Therapeutics, Fate Therapeutics Christopher E. Barbieri Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Coinventor on a patent application filed regarding SPOP mutations in prostate cancer by Weill Cornell Medicine Brian D. Robinson Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol-Myers Squibb Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Methods for diagnosing and treating prostate cancer Allyson J. Ocean Consulting or Advisory Role: Celgene, Tyme Speakers’ Bureau: Daiichi Sankyo Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Daiichi Sankyo Ana Molina Honoraria: American Society of Clinical Oncology Consulting or Advisory Role: Eisai, Exelixis, Novartis, Janssen Oncology Manish A. Shah Consulting or Advisory Role: Astellas Pharma, Eli Lilly Research Funding: Gilead Sciences (Inst), Merck (Inst), Boston Biomedical (Inst), Oncolys BioPharma (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst) David M. Nanus Consulting or Advisory Role: Genentech Research Funding: Novartis (Inst), Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Zenith Epigenetics (Inst) Qiulu Pan Employment: Caris Life Sciences Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Caris Life Sciences Francesca Demichelis Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Co-inventor on a patent filed by the University of Michigan and Brigham and Women’s Hospital covering the diagnostic and therapeutic fields for ETS fusions in prostate cancer, diagnostic field licensed to Gen-Probe Scott T. Tagawa Consulting or Advisory Role: Medivation, Astellas Pharma, Dendreon, Janssen Oncology, Bayer, Genentech, Endocyte, Immunomedics, Karyopharm Therapeutics, AbbVie, Tolmar, QED, Amgen, Sanofi, Pfizer Research Funding: Eli Lilly (Inst), Sanofi (Inst), Janssen Oncology (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), Progenics (Inst), Millennium Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Dendreon (Inst), Rexahn Pharmaceuticals (Inst), Bayer (Inst), Genentech (Inst), Newlink Genetics (Inst), Inovio Pharmaceuticals (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Immunomedics (Inst), Novartis (Inst), AVEO (Inst), Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst), Merck (Inst), Stem CentRx (Inst), Karyopharm Therapeutics (Inst), AbbVie (Inst), Medivation (Inst), Endocyte (Inst), Exelixis (Inst), Clovis Oncology (Inst) Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Sanofi, Immunomedics, Amgen Wei Song Employment: Genentech (I), Cytokinetics (I) Honoraria: Foundation Medicine, Loxo Consulting or Advisory Role: Foundation Medicine, Loxo Juan Miguel Mosquera Research Funding: Personal Genome Diagnostics Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Personal Genome Diagnostics Mark A. Rubin Honoraria: F Hoffmann-La Roche, Novartis, Astellas Pharma Research Funding: Eli Lilly, Janssen Oncology, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: US Patent (7,767,393 and 7,229,774), Expression Profile of Prostate Cancer, 2007; US Patent (7,332,290), Detection of AMACR Cancer Markers in Urine, 2008; US Patent (7,718,369), Recurrent Gene Fusions in Prostate Cancer, 2010; US Patent (7,803,552 and 7,666,595), Biomarkers for Predicting Prostate Cancer Progression, 2010; US Patent (7,981,609 B2), Methods for Identifying and Using SNP Panels, 2011; US Patent (8,106,037 B2), Identification and Treatment of Estrogen Responsive PCa, 2012; US Patent (9,090,899 B2), Methods of Diagnosing and Treating Prostate Cancer Characterized by NDRG1-ERG Fusion, 2015; US Patent (9,458,213 B2), Compositions and Methods for Diagnosing Prostate Cancer Based on Detection of SLC45A3-ELK4 Fusion Transcript, 2016; US Patent (9,568,483 B2), Molecular Subtyping, Prognosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer, 2017; US Patent (9,678,077 B2), ERG/TFF3/HMWCK Triple Immunostain for Detection of Prostate Cancer, 2017; US Patent (61,408,341), Exploration of Novel Gene Fusion in Prostate Cancer by RNA-Seq Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: F Hoffmann-La Roche, Novartis, Astellas Pharma Olivier Elemento Stock and Other Ownership Interests: Volastra, Owkin, One Three Biotech Himisha Beltran Consulting or Advisory Role: Janssen Oncology, Genzyme, GlaxoSmithKline, AbbVie, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca Research Funding: Janssen Oncology (Inst), AbbVie (Inst), Stemcentrx (Inst), Eli Lilly (Inst) Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Janssen Oncology No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integration of whole-exome and anchored PCR-based next generation sequencing significantly increases detection of actionable alterations in precision oncology.Transl Oncol. 2021 Jan;14(1):100944. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100944. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33190043 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Exome Sequencing of Metastatic Cancer and Biomarkers of Treatment Response.JAMA Oncol. 2015 Jul;1(4):466-74. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1313. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26181256 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, and TP53 in families at high risk of breast cancer.JAMA. 2006 Mar 22;295(12):1379-88. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.12.1379. JAMA. 2006. PMID: 16551709
-
Concordance of Circulating Tumor DNA and Matched Metastatic Tissue Biopsy in Prostate Cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017 Dec 1;109(12):djx118. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx118. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017. PMID: 29206995 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma is associated with BRCA2 germline mutations: a case report and literature review.Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(7):949-955. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1595274. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31002019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional comparison of exome capture-based methods for transcriptomic profiling of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumors.NPJ Genom Med. 2021 Aug 12;6(1):66. doi: 10.1038/s41525-021-00231-7. NPJ Genom Med. 2021. PMID: 34385467 Free PMC article.
-
Digital spatial profiling identifies phospho-JNK as a biomarker for early risk stratification of aggressive prostate cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 5;15:1572299. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1572299. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40538844 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Platelet-Related Prognostic Model for Colorectal Cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 1;13:904168. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.904168. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35719389 Free PMC article.
-
SLFN11 Expression in Advanced Prostate Cancer and Response to Platinum-based Chemotherapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 May;19(5):1157-1164. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-0926. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32127465 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Circulating Tumour DNA (ctDNA) for Measurement of Therapy Predictive Biomarkers in Patients with Cancer.J Pers Med. 2022 Jan 13;12(1):99. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010099. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35055414 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

