Imaging anatomy of the retrotympanum: variants and their surgical implications
- PMID: 31593485
- PMCID: PMC6948074
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20190677
Imaging anatomy of the retrotympanum: variants and their surgical implications
Abstract
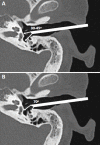
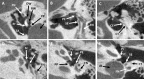
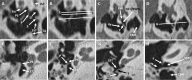
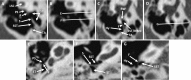
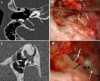
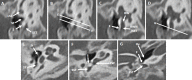
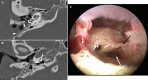
The retrotympanic anatomy is complex and variable but has received little attention in the radiological literature. With advances in CT technology and the application of cone beam CT to temporal bone imaging, there is now a detailed depiction of the retrotympanic bony structures.With the increasing use of endoscopes in middle ear surgery, it is important for the radiologist to appreciate the nomenclature of the retrotympanic compartments in order to aid communication with the surgeon. For instance, in the context of cholesteatoma, clear imaging descriptions of retrotympanic variability and pathological involvement are valuable in pre-operative planning.The endoscopic anatomy has recently been described and the variants classified. The retrotympanum is divided into medial and lateral compartments with multiple described potential sinuses separated by bony crests.This pictorial review will describe the complex anatomy and variants of the retrotympanum. We will describe optimum reformatting techniques to demonstrate the structures of the retrotympanum and illustrate the associated anatomical landmarks and variants with CT. The implications of anatomical variants with regards to otologic surgery will be discussed.
Figures
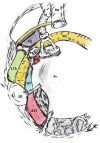







Similar articles
-
Endoscopic anatomy of the retrotympanum.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2013 Apr;46(2):179-88. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2012.10.003. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2013. PMID: 23566904 Review.
-
Inferior retrotympanum revisited: an endoscopic anatomic study.Laryngoscope. 2010 Sep;120(9):1880-6. doi: 10.1002/lary.20995. Laryngoscope. 2010. PMID: 20715093
-
Pyramidal eminence and subpyramidal space: an endoscopic anatomical study.Laryngoscope. 2010 Mar;120(3):557-64. doi: 10.1002/lary.20748. Laryngoscope. 2010. PMID: 20013839
-
Accuracy of High-Resolution Computed Tomography Compared to High-Definition Ear Endoscopy to Assess Cholesteatoma Extension.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023 Nov;169(5):1276-1281. doi: 10.1002/ohn.413. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023. PMID: 37418100
-
Novel Radiologic Approaches for Cholesteatoma Detection: Implications for Endoscopic Ear Surgery.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2021 Feb;54(1):89-109. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2020.09.011. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 33153729 Review.
Cited by
-
[Anatomical variants of the petrous bone].Radiologie (Heidelb). 2025 Aug;65(8):556-561. doi: 10.1007/s00117-025-01465-7. Epub 2025 May 30. Radiologie (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40445303 Review. German.
-
Guidelines for magnetic resonance imaging in pediatric head and neck pathologies: a multicentre international consensus paper.Neuroradiology. 2022 Jun;64(6):1081-1100. doi: 10.1007/s00234-022-02950-9. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Neuroradiology. 2022. PMID: 35460348
-
Analysis of tympanic sinus shape for purposes of intraoperative hearing monitoring: a microCT study.Surg Radiol Anat. 2022 Feb;44(2):323-331. doi: 10.1007/s00276-021-02859-7. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Surg Radiol Anat. 2022. PMID: 34817623 Free PMC article.
-
The posterior-inferior recess of the sinus tympani - radioanatomical investigation for purposes of endoscopic otosurgery in children under five.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jul 12. doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09558-8. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40652133
-
Radioanatomical evaluation of the subtympanic sinus in children under five years old and its clinical implications - high resolution computed tomography study.Surg Radiol Anat. 2024 Dec;46(12):1965-1975. doi: 10.1007/s00276-024-03508-5. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Surg Radiol Anat. 2024. PMID: 39441351 Free PMC article.

