Prevalence and correlates of partner violence among adolescent girls and young women: Evidence from baseline data of a cluster randomised trial in Tanzania
- PMID: 31593577
- PMCID: PMC6782098
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222950
Prevalence and correlates of partner violence among adolescent girls and young women: Evidence from baseline data of a cluster randomised trial in Tanzania
Abstract
Background: Little has been documented about partner violence among adolescent girls and young women (AGYW) who are out of school, a factor associated with HIV acquisition. To understand areas for prioritising HIV prevention intervention efforts, we explored the prevalence and correlates of partner violence among out of school AGYW in Shinyanga, Tanzania.
Methods: A cross-sectional analysis of data from AGYW aged 15-23 years recruited in a cluster randomised trial conducted between October and December 2017 was used to examine correlates of partner violence. Data were collected through an Audio Computer-Assisted Self-interview. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the association.
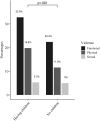
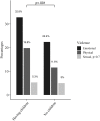
Results: 2276 (75.5%) AGYW were sexually active. Of these, 816 (35.9%) reported having experienced violence from partners in the last six months. After adjusting for other covariates, being formerly married (AOR = 1.55, 95% CI:1.02, 2.37), having children (AOR = 1.79, 95% CI:1.47, 2.16), anxiety and depression symptoms (AOR = 3.27, 95%CI: 2.15, 4.96), having engaged in sex work in the past six months (AOR = 1.92, 95% CI: 1.45, 2.53) and economic deprivation (AOR = 1.61, 95% CI: 1.34,1.92) were significantly associated with partner violence.
Conclusions: Almost one in three sexually active AGYW had experienced partner violence in the 6 months preceding the survey. The findings underscore the need for future research to focus on understanding the reasons and dynamics underlying high level of partner violence among AGYW. Furthermore, there is a need for implementing intervention programs that aim to reduce economic deprivation among AGYWs and address social norms and structures perpetuating violence against AGYW.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov-ID NCT03597243.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ellsberg M, Jansen HA, Heise L, Watts CH, Garcia-Moreno C. Intimate partner violence and women’s physical and mental health in the WHO multi-country study on women’s health and domestic violence: an observational study. The Lancet. 2008;371(9619):1165–72. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Moreno C, Jansen HA, Ellsberg M, Heise L, Watts CH. Prevalence of intimate partner violence: findings from the WHO multi-country study on women’s health and domestic violence. The Lancet. 2006;368(9543):1260–9. - PubMed
-
- WHO. WHO/WHD Violence against women: a priority health issue. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous