A Semiquantitative Scoring System May Allow Biopsy Diagnosis of Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
- PMID: 31593583
- PMCID: PMC7571487
- DOI: 10.1093/ajcp/aqz149
A Semiquantitative Scoring System May Allow Biopsy Diagnosis of Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 Jan 2;153(2):286. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqz197. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31786603 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to devise reproducible biopsy criteria for distinguishing pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) from non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
Methods: Tissue microarrays of LCNEC and NSCLC were generated from resection specimens and used as biopsy surrogates. They were stained for neuroendocrine markers, Ki-67, napsin-A, and p40, and independently analyzed by standardized morphologic criteria by four pathologists. Tumors were scored based on morphology, neuroendocrine marker expression, and Ki-67 proliferative index.
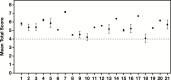
Results: The average total score for LCNEC was significantly higher than for NSCLC (5.65 vs 0.51, P < .0001). Utilizing a cutoff score of 4 or higher showed 100% sensitivity and 99% specificity for LCNEC diagnosis, with an excellent agreement among four pathologists (98%).
Conclusions: The proposed semiquantitative approach based on a combination of specific morphologic and immunophenotypic features may be a useful tool for biopsy diagnosis of LCNEC.
Keywords: Biopsy diagnosis; Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung; Scoring criteria.
© American Society for Clinical Pathology, 2019. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Is the sum of positive neuroendocrine immunohistochemical stains useful for diagnosis of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) on biopsy specimens?Histopathology. 2019 Mar;74(4):555-566. doi: 10.1111/his.13800. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Histopathology. 2019. PMID: 30485478 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological diagnosis of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Feb;9(2):273-277. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12576. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29271588 Free PMC article.
-
Ki-67 Index of 55% Distinguishes Two Groups of Bronchopulmonary Pure and Composite Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinomas with Distinct Prognosis.Neuroendocrinology. 2021;111(5):475-489. doi: 10.1159/000508376. Epub 2020 May 4. Neuroendocrinology. 2021. PMID: 32365350
-
Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2022 Oct 11;28:1610730. doi: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610730. eCollection 2022. Pathol Oncol Res. 2022. PMID: 36304941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung: an aggressive neuroendocrine lung cancer.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006 Fall;18(3):206-10. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2006.08.007. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006. PMID: 17185180 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of the 5th WHO Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Lung Carcinoma in Small Lung Biopsies in a Tertiary Care Center: Is Insecurity of Pathologists for the Accurate Diagnosis Justified?Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;14(18):2090. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14182090. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335769 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Clinical Translation of Small-Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;17(2):255. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020255. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcomes with Sublobar Resection vs Lobectomy in Patients With cT1N0M0 Large-cell Neuroendocrine Cancer.Ann Thorac Surg Short Rep. 2024 Dec 13;3(2):287-292. doi: 10.1016/j.atssr.2024.12.003. eCollection 2025 Jun. Ann Thorac Surg Short Rep. 2024. PMID: 40525179 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical activity of pembrolizumab with or without chemotherapy in advanced pulmonary large-cell and large-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas: a multicenter retrospective cohort study.BMC Cancer. 2023 May 16;23(1):443. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10952-w. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37189075 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of peripheral blood neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in advanced-stage pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and its association with the immune-related tumour microenvironment.Br J Cancer. 2021 Mar;124(5):925-932. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01188-7. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33250511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Travis WD, Linnoila RI, Tsokos MG, et al. Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung with proposed criteria for large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: an ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and flow cytometric study of 35 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991;15:529-553. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink KH, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. 3rd ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2004.
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2015. - PubMed
-
- Derks JL, Leblay N, Thunnissen E, et al. ; PALGA-Group Molecular subtypes of pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma predict chemotherapy treatment outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:33-42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

