Stimulation of Collateral Vessel Growth by Inhibition of Galectin 2 in Mice Using a Single-Domain Llama-Derived Antibody
- PMID: 31594443
- PMCID: PMC6818022
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012806
Stimulation of Collateral Vessel Growth by Inhibition of Galectin 2 in Mice Using a Single-Domain Llama-Derived Antibody
Abstract
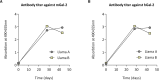
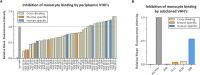
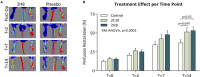
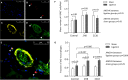
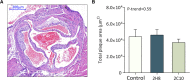
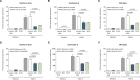
Background In the presence of arterial stenosis, collateral artery growth (arteriogenesis) can alleviate ischemia and preserve tissue function. In patients with poorly developed collateral arteries, Gal-2 (galectin 2) expression is increased. In vivo administration of Gal-2 inhibits arteriogenesis. Blocking of Gal-2 potentially stimulates arteriogenesis. This study aims to investigate the effect of Gal-2 inhibition on arteriogenesis and macrophage polarization using specific single-domain antibodies. Methods and Results Llamas were immunized with Gal-2 to develop anti-Gal-2 antibodies. Binding of Gal-2 to monocytes and binding inhibition of antibodies were quantified. To test arteriogenesis in vivo, Western diet-fed LDLR.(low-density lipoprotein receptor)-null Leiden mice underwent femoral artery ligation and received treatment with llama antibodies 2H8 or 2C10 or with vehicle. Perfusion restoration was measured with laser Doppler imaging. In the hind limb, arterioles and macrophage subtypes were characterized by histology, together with aortic atherosclerosis. Llama-derived antibodies 2H8 and 2C10 strongly inhibited the binding of Gal-2 to monocytes (93% and 99%, respectively). Treatment with these antibodies significantly increased perfusion restoration at 14 days (relative to sham, vehicle: 41.3±2.7%; 2H8: 53.1±3.4%, P=0.016; 2C10: 52.0±3.8%, P=0.049). In mice treated with 2H8 or 2C10, the mean arteriolar diameter was larger compared with control (vehicle: 17.25±4.97 μm; 2H8: 17.71±5.01 μm; 2C10: 17.84±4.98 μm; P<0.001). Perivascular macrophages showed a higher fraction of the M2 phenotype in both antibody-treated animals (vehicle: 0.49±0.24; 2H8: 0.73±0.15, P=0.007; 2C10: 0.75±0.18, P=0.006). In vitro antibody treatment decreased the expression of M1-associated cytokines compared with control (P<0.05 for each). Atherosclerotic lesion size was comparable between groups (overall P=0.59). Conclusions Inhibition of Gal-2 induces a proarteriogenic M2 phenotype in macrophages, improves collateral artery growth, and increases perfusion restoration in a murine hind limb model.
Keywords: antibody; collateral circulation; macrophage; murine model; perfusion defect.
Figures
References
-
- Schaper W, Buschmann I. Arteriogenesis, the good and bad of it. Eur Heart J. 1999;20:1297–1299. - PubMed
-
- Seiler C, Stoller M, Pitt B, Meier P. The human coronary collateral circulation: development and clinical importance. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2674–2682. - PubMed
-
- Ripley DP, Gosling OE, Bhatia L, Peebles CR, Shore AC, Curzen N, Bellenger NG. The relationship between the contralateral collateral supply and myocardial viability on cardiovascular magnetic resonance: can the angiogram predict functional recovery? Int J Cardiol. 2014;177:362–367. - PubMed
-
- Hara M, Sakata Y, Nakatani D, Suna S, Nishino M, Sato H, Kitamura T, Nanto S, Hori M, Komuro I; OACIS Investigators . Impact of coronary collaterals on in‐hospital and 5‐year mortality after ST‐elevation myocardial infarction in the contemporary percutaneous coronary intervention era: a prospective observational study. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e011105. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meier P, Gloekler S, Zbinden R, Beckh S, de Marchi SF, Zbinden S, Wustmann K, Billinger M, Vogel R, Cook S, Wenaweser P, Togni M, Windecker S, Meier B, Seiler C. Beneficial effect of recruitable collaterals: a 10‐year follow‐up study in patients with stable coronary artery disease undergoing quantitative collateral measurements. Circulation. 2007;116:975–983. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

