Negativity-bias in forming beliefs about own abilities
- PMID: 31594967
- PMCID: PMC6783436
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-50821-w
Negativity-bias in forming beliefs about own abilities
Abstract
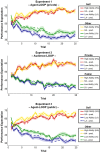
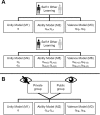
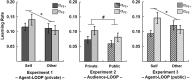
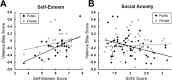
During everyday interactions people constantly receive feedback on their behavior, which shapes their beliefs about themselves. While classic studies in the field of social learning suggest that people have a tendency to learn better from good news (positivity bias) when they perceive little opportunities to immediately improve their own performance, we show updating is biased towards negative information when participants perceive the opportunity to adapt their performance during learning. In three consecutive experiments we applied a computational modeling approach on the subjects' learning behavior and reveal the negativity bias was specific for learning about own compared to others' performances and was modulated by prior beliefs about the self, i.e. stronger negativity bias in individuals lower in self-esteem. Social anxiety affected self-related negativity biases only when individuals were exposed to a judging audience thereby potentially explaining the persistence of negative self-images in socially anxious individuals which commonly surfaces in social settings. Self-related belief formation is therefore surprisingly negatively biased in situations suggesting opportunities to improve and this bias is shaped by trait differences in self-esteem and social anxiety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures