Intact value-based decision-making during intertemporal choice in women with remitted anorexia nervosa? An fMRI study
- PMID: 31595737
- PMCID: PMC7828910
- DOI: 10.1503/jpn.180252
Intact value-based decision-making during intertemporal choice in women with remitted anorexia nervosa? An fMRI study
Abstract
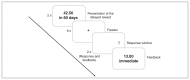
Background: Extreme restrictive food choice in anorexia nervosa is thought to reflect excessive self-control and/or abnormal reward sensitivity. Studies using intertemporal choice paradigms have suggested an increased capacity to delay reward in anorexia nervosa, and this may explain an unusual ability to resist immediate temptation and override hunger in the long-term pursuit of thinness. It remains unclear, however, whether altered delay discounting in anorexia nervosa constitutes a state effect of acute illness or a trait marker observable after recovery.
Methods: We repeated the analysis from our previous fMRI investigation of intertemporal choice in acutely underweight patients with anorexia nervosa in a sample of weight-recovered women with anorexia nervosa (n = 36) and age-matched healthy controls (n = 36) who participated in the same study protocol. Follow-up analyses explored functional connectivity separately in both the weight-recovered/healthy controls sample and the acute/healthy controls sample.
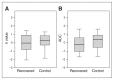
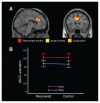
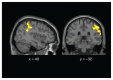
Results: In contrast to our previous findings in acutely underweight patients with anorexia nervosa, we found no differences between weight-recovered patients with anorexia nervosa and healthy controls at either behavioural or neural levels. New analysis of data from the acute/healthy controls sample sample revealed increased coupling between dorsal anterior cingulate cortex and posterior brain regions as a function of decision difficulty, supporting the hypothesis of altered neural efficiency in the underweight state.
Limitations: This was a cross-sectional study, and the results may be task-specific.
Conclusion: Although our results underlined previous demonstrations of divergent temporal reward discounting in acutely underweight patients with anorexia nervosa, we found no evidence of alteration in patients with weight-recovered anorexia nervosa. Together, these findings suggest that impaired valuebased decision-making may not constitute a defining trait variable or “scar” of the disorder.
© 2020 Joule Inc. or its licensors
Conflict of interest statement
V. Roessner has received payment for consulting and writing activities, independent of the current work, from Lilly, Novartis and Shire Pharmaceuticals; lecture honoraria from Lilly, Novartis, Shire Pharmaceuticals and Medice Pharma; and support for research from Shire and Novartis. He has carried out (and is currently carrying out) clinical trials in cooperation with the Novartis, Shire and Otsuka. J. King, F. Bernardoni, D. Geisler, F. Ritschel, A. Doose, S. Pauligk, K. Pásztor, K. Weidner, M. Smolka and S. Ehrlich declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- O’Hara CB, Campbell IC, Schmidt U. A reward-centred model of anorexia nervosa: a focussed narrative review of the neurological and psychophysiological literature. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015;52:131–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

