Neuronal network remodeling and Wnt pathway dysregulation in the intra-hippocampal kainate mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 31596871
- PMCID: PMC6785072
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215789
Neuronal network remodeling and Wnt pathway dysregulation in the intra-hippocampal kainate mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
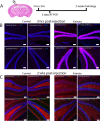
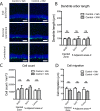
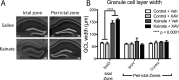
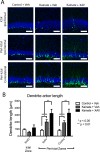
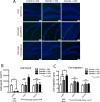
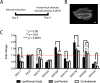
Mouse models of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy recapitulate aspects of human epilepsy, which is characterized by neuronal network remodeling in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Observational studies suggest that this remodeling is associated with altered Wnt pathway signaling, although this has not been experimentally examined. We used the well-characterized mouse intrahippocampal kainate model of temporal lobe epilepsy to examine associations between hippocampal neurogenesis and altered Wnt signaling after seizure induction. Tissue was analyzed using immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy, and gene expression analysis was performed by RT-qPCR on RNA extracted from anatomically micro-dissected dentate gyri. Seizures increased neurogenesis and dendritic arborization of newborn hippocampal dentate granule cells in peri-ictal regions, and decreased neurogenesis in the ictal zone, 2-weeks after kainate injection. Interestingly, administration of the novel canonical Wnt pathway inhibitor XAV939 daily for 2-weeks after kainate injection further increased dendritic arborization in peri-ictal regions after seizure, without an effect on baseline neurogenesis in control animals. Transcriptome analysis of dentate gyri demonstrated significant canonical Wnt gene dysregulation in kainate-injected mice across all regions for Wnt3, 5a and 9a. Intriguingly, certain Wnt genes demonstrated differential patterns of dysregulation between the ictal and peri-ictal zones, most notably Wnt5B, 7B and DKK-1. Together, these results demonstrate regional variation in Wnt pathway dysregulation early after seizure induction, and surprisingly, suggest that some Wnt-mediated effects might actually temper aberrant neurogenesis after seizures. The Wnt pathway may therefore provide suitable targets for novel therapies that prevent network remodeling and the development of epileptic foci in high-risk patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

