MicroRNAs and Epigenetics Strategies to Reverse Breast Cancer
- PMID: 31597272
- PMCID: PMC6829616
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8101214
MicroRNAs and Epigenetics Strategies to Reverse Breast Cancer
Abstract
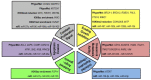
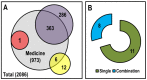
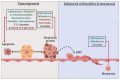
Breast cancer is a sporadic disease with genetic and epigenetic components. Genomic instability in breast cancer leads to mutations, copy number variations, and genetic rearrangements, while epigenetic remodeling involves alteration by DNA methylation, histone modification and microRNAs (miRNAs) of gene expression profiles. The accrued scientific findings strongly suggest epigenetic dysregulation in breast cancer pathogenesis though genomic instability is central to breast cancer hallmarks. Being reversible and plastic, epigenetic processes appear more amenable toward therapeutic intervention than the more unidirectional genetic alterations. In this review, we discuss the epigenetic reprogramming associated with breast cancer such as shuffling of DNA methylation, histone acetylation, histone methylation, and miRNAs expression profiles. As part of this, we illustrate how epigenetic instability orchestrates the attainment of cancer hallmarks which stimulate the neoplastic transformation-tumorigenesis-malignancy cascades. As reversibility of epigenetic controls is a promising feature to optimize for devising novel therapeutic approaches, we also focus on the strategies for restoring the epistate that favor improved disease outcome and therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: epigenetic editing; epigenetics diet; estrogen receptor; hTERT; microRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer Fact Sheets by International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and World Health Organization (WHO) [(accessed on 20 June 2019)]; Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/20-Breast-fact-sheet.pdf.
-
- American Cancer Society . Global Cancer Facts & Figures. 4th ed. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2018. pp. 12–15.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

