THE RELIABILITY OF THE STAR EXCURSION BALANCE TEST AND LOWER QUARTER Y-BALANCE TEST IN HEALTHY ADULTS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
- PMID: 31598406
- PMCID: PMC6769278
THE RELIABILITY OF THE STAR EXCURSION BALANCE TEST AND LOWER QUARTER Y-BALANCE TEST IN HEALTHY ADULTS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Abstract
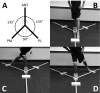
Background: Dynamic balance is often an important criterion used during lower extremity musculoskeletal injury prediction, prevention, and rehabilitation processes. Methods to assess lower extremity dynamic balance include the Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) and Lower Quarter Y-Balance Test (YBT). Due to the importance of dynamic balance it is imperative to establish reliable quantification techniques.
Purpose: To conduct a systematic review to assess the reliability and responsiveness of the SEBT/YBT.
Study design: Systematic Review.
Methods: Electronic databases (PubMed, MEDLINE, CINAHL, and SPORTDiscus) were searched from inception to August 2018. Included studies examined the intra- and inter-rater reliability of the SEBT/YBT in healthy adults. Two investigators independently assessed methodological quality, level of evidence and strength of recommendation with the Qualtiy Appraisal of Reliability Studies (QAREL) scale. Relative intra and inter-rater reliability was examined through intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) and responsiveness was evaluated through minimal detectable change (MDC). Data was analyzed based on reach direction (Anterior, Posteromedial, and Posterolateral) and normalization (normalized and non-normalized). Additionally, data were then synthesized using the strength of recommendation taxonomy to provide a grade of recommendation.
Results: A total of nine studies were included in this review. Six studies examined the inter-rater reliability and seven assessed intra-rater reliability. The included studies had a median QAREL score of 66.89% (range = 55.56% to 75.00%) and 59.03% (range = 33.33 to 66.67%) for inter and intra-rater reliability respectively. Median ICC values for inter-rater reliability were 0.88 (Range = 0.83 - 0.96), 0.87 (range = 0.80 - 1.00), and 0.88 (range = 0.73 - 1.00) for the anterior, posteromedial, and posterolateral directions respectively. Median ICC values for intra-rater reliability were 0.88 (Range = 0.84 - 0.93), 0.88 (Range = 0.85 - 0.94), and 0.90 (Range = 0.68 - 0.94) for the anterior, posteromedial, and posterolateral directions, respectively.
Conclusions: There is grade A evidence to support that the SEBT/YBT have excellent inter and intra-rater reliability when used in healthy adults. Furthermore, minimal detectable change values have been provided that can be used in practice to aid clinical decision making. Future research is needed to assess the reliability, responsiveness, and validity of the SEBT/YBT in pathologic populations.
Level of evidence: 1a.
Keywords: Dynamic balance; inter-rater reliability; intra-rater reliability; movement system; test-retest reliability.
© 2019 by the Sports Physical Therapy Section.
Figures
References
-
- Kraus JF Conroy C. Mortality and morbidity from injuries in sports and recreation. Annu Rev Public Heal. 1984;5(1):163-192. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials