The Effect of Ras Homolog C/Rho-Associated Coiled-Protein Kinase (Rho/ROCK) Signaling Pathways on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Myeloma Cells
- PMID: 31599230
- PMCID: PMC6798802
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.915998
The Effect of Ras Homolog C/Rho-Associated Coiled-Protein Kinase (Rho/ROCK) Signaling Pathways on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Myeloma Cells
Abstract
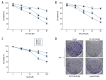
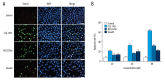
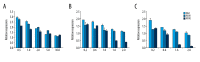
BACKGROUND The aim of this study was to explore the impact of Ras homolog C/Rho-associated coiled-protein kinase (Rho/ROCK) signaling pathways intervention on biological characteristics of the human multiple myeloma cell lines RPMI-8226 and U266 cells, and to investigate the expression of RhoC, ROCK1, and ROCK2 in RPMI-8226 and U266 cells. MATERIAL AND METHODS RPMI8226 and U266 cell lines were treated by 5-aza-2-deoxycytidine (5-Aza-Dc), trichostatin A (TSA), RhoA inhibitor CCG-1423, Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766, and ROCK inhibitor fasudil. Cell proliferation was examined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay and clone formation. Cell apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry and TUNEL assay. The mRNA and protein expressions of RhoC, ROCK1, and ROCK2 were detected by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blot, respectively. RESULTS CCG-1423, NSC23766, and fasudil could significantly inhibit the proliferation of RPMI8226 and U266 cells. The inhibitory effect was dose- and time-dependent within a certain concentration range (P<0.05). After treatment with CCG-1423, NSC23766, and fasudil for 24 hours, the apoptosis rates of RPMI8226 and U266 cells were significantly higher than those of the control group, which were dose-dependent (P<0.05). Compared with the control group, the mRNA and protein expressions of RhoC, ROCK1, and ROCK2 in RPMI8226 and U266 cells were significantly decreased with single 5-Aza-Dc or TSA treatment. However, the effects were obviously stronger after combined treatment of 5-Aza-CdR and TSA (P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS We found that 5-Aza-Dc and TSA can effectively decrease the mRNA and protein expressions of RhoC, ROCK1, and ROCK2. Furthermore, Rho and ROCK inhibitors significantly inhibit cell growth and induce cell apoptosis in the human multiple myeloma cell lines RPMI-8226 and U266.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


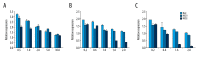


Similar articles
-
Effect of 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine combined with trichostatin A on RPMI-8226 cell proliferation, apoptosis and DLC-1 gene expression.Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Apr;22(2):357-63. doi: 10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2014.02.017. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24763005
-
Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, suppresses glioblastoma cell line progression in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Jun 1;9(11):875-84. doi: 10.4161/cbt.9.11.11634. Epub 2010 Jun 26. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20364104
-
Rho-Kinase inhibitor fasudil suppresses high glucose-induced H9c2 cell apoptosis through activation of autophagy.Cardiovasc Ther. 2016 Oct;34(5):352-9. doi: 10.1111/1755-5922.12206. Cardiovasc Ther. 2016. PMID: 27333569
-
Functions of Rho family of small GTPases and Rho-associated coiled-coil kinases in bone cells during differentiation and mineralization.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 May;1861(5 Pt A):1009-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28188861 Review.
-
Rho kinases in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology: the effect of fasudil.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;62(4):341-54. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182a3718f. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23921309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hsa_circ_0041268 promotes NSCLC progress by sponging miR-214-5p/ROCK1.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24262. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24262. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35212425 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Rac1 in p53-Related Proliferation and Drug Sensitivity in Multiple Myeloma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 29;17(3):461. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030461. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941828 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK1 knockdown inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer progression by activating the LATS2-JNK signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jun 17;12(12):12160-12174. doi: 10.18632/aging.103386. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32554853 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Small Molecular Compound AE-848 Potently Induces Human Multiple Myeloma Cell Apoptosis by Modulating the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathways.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Dec 22;13:13063-13075. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S270090. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33376355 Free PMC article.
-
Sagacious confucius' pillow elixir ameliorates Dgalactose induced cognitive injury in mice via estrogenic effects and synaptic plasticity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 28;13:971385. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.971385. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tuscano JM. Multiple myeloma: Epidemiology and therapeutic options. Manag Care. 2008;17:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Madaule P, Axel R. A novel Ras-related gene family. Cell. 1985;41:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Morris SW, Valentine MB, Kirstein MN, Huebner K. Reassignment of the human ARH9 RAS-related gene to chromosome 1p13–p21. Genomics. 1993;15:677–79. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

