Role of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Study of the International Radiosurgery Research Foundation (IRRF)
- PMID: 31599324
- PMCID: PMC7780439
- DOI: 10.1093/neuros/nyz428
Role of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Study of the International Radiosurgery Research Foundation (IRRF)
Abstract
Background: Despite a high incidence of brain metastases in patients with small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), limited data exist on the use of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), specifically Gamma Knife™ radiosurgery (Elekta AB), for SCLC brain metastases.
Objective: To provide a detailed analysis of SCLC patients treated with SRS, focusing on local failure, distant brain failure, and overall survival (OS).
Methods: A multi-institutional retrospective review was performed on 293 patients undergoing SRS for SCLC brain metastases at 10 medical centers from 1991 to 2017. Data collection was performed according to individual institutional review boards, and analyses were performed using binary logistic regression, Cox-proportional hazard models, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, and competing risks analysis.
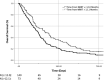
Results: Two hundred thirty-two (79%) patients received SRS as salvage following prior whole-brain irradiation (WBRT) or prophylactic cranial irradiation, with a median marginal dose of 18 Gy. At median follow-up after SRS of 6.4 and 18.0 mo for surviving patients, the 1-yr local failure, distant brain failure, and OS were 31%, 49%, and 28%. The interval between WBRT and SRS was predictive of improved OS for patients receiving SRS more than 1 yr after initial treatment (21%, <1 yr vs 36%, >1 yr, P = .01). On multivariate analysis, older age was the only significant predictor for OS (hazard ratio 1.63, 95% CI 1.16-2.29, P = .005).
Conclusion: SRS plays an important role in the management of brain metastases from SCLC, especially in salvage therapy following WBRT. Ongoing prospective trials will better assess the value of radiosurgery in the primary management of SCLC brain metastases and potentially challenge the standard application of WBRT in SCLC patients.
Keywords: Gamma Knife; Small-cell lung cancer; Stereotactic radiosurgery; Whole-brain radiation.
Copyright © 2019 by the Congress of Neurological Surgeons.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery with and without whole-brain radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed brain metastases.J Neurosurg. 2014 Dec;121 Suppl:84-90. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.GKS14972. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25434941
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery to the resection bed for intracranial metastases and risk of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis.J Neurosurg. 2014 Dec;121 Suppl:75-83. doi: 10.3171/2014.6.GKS14708. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25434940
-
Gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery as salvage therapy after failure of whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with small-cell lung cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 May 1;83(1):e53-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.11.059. Epub 2012 Feb 17. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22342297 Free PMC article.
-
Should Stereotactic Radiosurgery Be Considered for Salvage of Intracranial Recurrence after Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation or Whole Brain Radiotherapy in Small Cell Lung Cancer? A Population-Based Analysis and Literature Review.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2020 Mar;51(1):75-87.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2019.10.001. Epub 2019 Nov 20. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2020. PMID: 31759940 Review.
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) alone versus whole brain radiotherapy plus SRS in patients with 1 to 4 brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer stratified by the graded prognostic assessment: A meta-analysis (PRISMA) of randomized control trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(33):e11777. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011777. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30113464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Memantine in the Prevention of Radiation-Induced Brain Damage: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 31;14(11):2736. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112736. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of treatment response in patients with brain metastasis receiving stereotactic radiosurgery based on pre-treatment multimodal MRI radiomics and clinical risk factors: A machine learning model.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 13;13:1114194. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1114194. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36994193 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation in the MRI Era for Patients With Limited Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 28;12:833478. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.833478. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35296010 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world treatment patterns and outcomes in small-cell lung cancer: a systematic literature review.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Jun;13(6):3692-3707. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-3034. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 34277061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiosurgery for small-cell lung cancer brain metastases: a review.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Oct;12(10):6234-6239. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2020.03.90. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 33209462 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nugent JL, Bunn PA, Jr Matthews MJ et al. . CNS metastases in small cell bronchogenic carcinoma: increasing frequency and changing pattern with lengthening survival. Cancer. 1979;44(5):1885-1893. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi T, Yamanaka T, Seto T et al. . Prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(5):663-671. - PubMed
-
- Robin TP, Jones BL, Amini A et al. . Radiosurgery alone is associated with favorable outcomes for brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2018;120:88-90. - PubMed
-
- Wegner RE, Olson AC, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Lundsford LD, Flickinger JC. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases from small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(3):e21-e27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

