Microwave ablation as local consolidative therapy for patients with extracranial oligometastatic EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer without progression after first-line EGFR-TKIs treatment
- PMID: 31599340
- PMCID: PMC11804293
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-019-03043-6
Microwave ablation as local consolidative therapy for patients with extracranial oligometastatic EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer without progression after first-line EGFR-TKIs treatment
Abstract
Objectives: Evidence from multiple clinical trials showed that local consolidative therapy (LCT) improved survival in oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. In the present study, we aim to explore the potential role of microwave ablation (MWA) as LCT for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant advanced NSCLC patients with extracranial oligometastasis.
Materials and methods: From January 2015 to December 2018, a total of 86 EGFR-mutant stage IIIB or IV NSCLC patients with extracranial oligometastasis were enrolled for retrospective analysis. MWA was used as LCT for all oligometastatic lesions and/or primary tumors in 34 patients without progression after first-line EGFR-TKIs therapy (consolidation group), while the other 52 patients received only TKIs until disease progression (monotherapy group). We calculated and compared the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of the two groups.
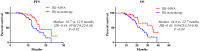
Results and conclusion: Patients with MWA consolidation therapy had significantly improved PFS (median 16.7 vs. 12.9 months, HR 0.44, 95% CI 0.22-0.88, P = 0.02) and OS (median: 34.8 vs. 22.7 months, HR 0.45, 95% CI 0.24-0.88, P = 0.04) than monotherapy group. MWA for LCT was identified as the independent predictive factor for better PFS (HR 0.46, 95% CI 0.37-0.82, P < 0.01) and OS (HR 0.57, 95% CI 0.33-0.91, P = 0.02). Most toxicities were mild and well tolerated. No patient had to discontinue EGFR-TKIs because of MWA complications. These findings suggest that MWA as local consolidative therapy after first-line EGFR-TKIs treatment leads to better disease control and survival than TKIs monotherapy in EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC patients with extracranial oligometastasis. MWA as a novel option of LCT might be considered for clinical management of these patients.
Keywords: EGFR-TKIs; Local consolidative therapy; Microwave ablation; Non-small cell lung cancer; Oligometastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjuvant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) for the treatment of people with resected stage I to III non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR mutation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 27;5(5):CD015140. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015140.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40421698 Review.
-
Outcomes of First-Line Microwave Ablation of Treatment-Naive Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2025 Jan;36(1):68-77.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2024.10.008. Epub 2024 Oct 19. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39428057
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3. PMID: 27223332 Updated.
-
Molecular testing, treatment patterns, and outcomes in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: the PISCES study.Future Oncol. 2025 Aug;21(19):2537-2547. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2529094. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40717496
-
Front-line therapy for brain metastases and non-brain metastases in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: a network meta-analysis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2023 Nov 5;136(21):2551-2561. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002468. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023. PMID: 37160733 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Radiofrequency ablation for stage <IIB non-small cell lung cancer: Opportunities, challenges, and the road ahead.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Nov;14(32):3181-3190. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15114. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37740563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index-based nomogram for lung carcinoma following microwave ablation -a real world single center study.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 20;14:1305262. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1305262. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38571504 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical value of local consolidative therapy for oligo-residual disease in PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors-treated non-small cell lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 17;15:1525236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1525236. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39742281 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation with Continued EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy Prolongs Disease Control in EGFR-Mutant Advanced Lung Cancers with Acquired Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Two Case Reports.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jul 13;13:6789-6793. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S257431. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32764966 Free PMC article.
-
Local ablative therapies in oligometastatic NSCLC-upfront or outback?-a narrative review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Jul;10(7):3446-3456. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-994. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34430379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Baere T, Tselikas L, Catena V, Buy X, Deschamps F, Palussiere J (2016) Percutaneous thermal ablation of primary lung cancer. Diagn Interv Imaging. 97(10):1019–1024 - PubMed
-
- Gomez DR, Blumenschein GR Jr, Lee JJ, Hernandez M, Ye R, Camidge DR et al (2016) Local consolidative therapy versus maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer without progression after first-line systemic therapy: a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 17(12):1672–1682 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gomez DR, Tang C, Zhang J, Blumenschein GR Jr, Hernandez M, Lee JJ et al (2019) Local consolidative therapy vs. maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 8:JCO1900201 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR (1995) Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol 13(1):8–10 - PubMed
-
- Inal A, Kodaz H, Odabas H, Duran AO, Seker MM, Inanc M et al (2018) Prognostic factors of patients who received chemotherapy after cranial irradiation for non-small cell lung cancer with brain metastases: a retrospective analysis of multicenter study (Anatolian Society of Medical Oncology). J Cancer Res Ther. 14(3):578–582 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous