Rebalancing Immune Homeostasis to Treat Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 31601519
- PMCID: PMC7136015
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2019.08.003
Rebalancing Immune Homeostasis to Treat Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
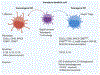
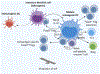
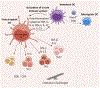
During homeostasis, interactions between tolerogenic dendritic cells (DCs), self-reactive T cells, and T regulatory cells (Tregs) contribute to maintaining mammalian immune tolerance. In response to infection, immunogenic DCs promote the generation of proinflammatory effector T cell subsets. When complex homeostatic mechanisms maintaining the balance between regulatory and effector functions become impaired, autoimmune diseases can develop. We discuss some of the newest advances on the mechanisms of physiopathologic homeostasis that can be employed to develop strategies to restore a dysregulated immune equilibrium. Some of these designs are based on selectively activating regulators of immunity and inflammation instead of broadly suppressing these processes. Promising approaches include the use of nanoparticles (NPs) to restore Treg control over self-reactive cells, aiming to achieve long-term disease remission, and potentially to prevent autoimmunity in susceptible individuals.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; immune regulation; immunotherapy; nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Rees F et al. (2017) The worldwide incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56 (11), 1945–1961. - PubMed
-
- Akbar AN et al. (2007) The dynamic co-evolution of memory and regulatory CD4+ T cells in the periphery. Nat Rev Immunol 7 (3), 231–7. - PubMed
-
- Surh CD and Sprent J (2012) TGF-beta puts the brakes on homeostatic proliferation. Nat Immunol 13 (7), 628–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

