Kangai Injection Combined with Platinum-based Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Stage III/IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review of 35 Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 31602279
- PMCID: PMC6775612
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.31928
Kangai Injection Combined with Platinum-based Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Stage III/IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review of 35 Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Objective: In an effort to inform evidence-based guidelines for clinical practice, we performed a meta-analysis to systematically evaluate the safety and efficacy of Kangai injection (KAI) plus platinum-based chemotherapy for stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Methods: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing KAI plus platinum-based chemotherapy (experimental group) to chemotherapy alone (control group) were electronically retrieved from the Cochrane Library, PubMed, EMbase, Web of Science, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Chinese Biological Medicine (CBM) Database, Wanfang Database, and the VIP Database for Chinese Technical Periodicals. RCTs published from the date of inception to July 5, 2018, were included. All trials were assessed for methodological quality in accordance with the Cochrane Reviewer's Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan5.3 Software and Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) 2.0. Results: The final analysis included 35 RCTs involving 2,618 patients. Our meta-analysis revealed that KAI combined with platinum-based chemotherapy was associated with significantly greater objective response rate (ORR) (RR=1.36, 95% CI: 1.25-1.49, P<0.00001) and disease control rate (DCR) (RR=1.14, 95% CI: 1.09-1.18, P<0.00001), improvements in quality of life (QOL) (RR=1.75, 95% CI: 1.59-1.93, P<0.00001), and decreases in the incidence of gastrointestinal reactions (RR=0.64, 95% CI: 0.54-0.77, P<0.00001), leukocytopenia (RR=0.54, 95% CI: 0.46-0.63, P<0.00001) and thrombocytopenia (RR=0.52, 95% CI: 0.36-0.76, P=0.0007) when compared with chemotherapy alone. In addition, combined treatment was associated with greater regulation of tumor immune function, as indicated by increases in the proportion of NK, CD3 + , and CD4 + cells (MD=2.27, 95% CI: 1.18-3.36, P<0.0001; MD=12.86, 95% CI: 11.64-14.08, P<0.00001; and MD=5.48, 95% CI: 2.68-8.28, P=0.0001) and decreases in the percentage of CD8 + cells (MD= -2.37, 95% CI from -4.51 to -0.23, P=0.03). Conclusions: From the available evidence, our results indicate that KAI plus platinum-based chemotherapy could be more effective in improving clinical efficacy, decreasing the incidence of adverse reactions and regulating the tumor immune function than chemotherapy alone in the treatment of stage III/IV NSCLC. Nevertheless, considering the limitations of the included studies, rigorous designed, high-quality, multicenter clinical trials are still need to further confirm the results.
Keywords: Kangai injection; Meta-analysis; non-small cell lung cancer; platinum-based chemotherapy; systematic review.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



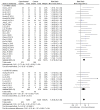





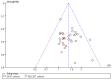
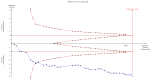

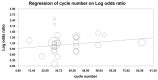
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Yip C, Blower PJ, Goh V, Landau DB, Cook GJR. Molecular imaging of hypoxia in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol I. 2015;42:956–76. - PubMed
-
- Johnson ML, Patel JD. Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapeutics as Maintenance of Response in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Semin Oncol. 2014;41:93–100. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

