Exercise-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in a Police Officer with Hereditary Renal Hypouricemia
- PMID: 31602378
- PMCID: PMC6738254
- DOI: 10.1159/000501877
Exercise-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in a Police Officer with Hereditary Renal Hypouricemia
Abstract
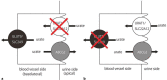
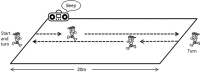
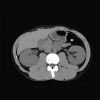
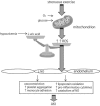
Hereditary renal hypouricemia is characterized by hypouricemia with hyper-uric acid clearance due to a defect in renal tubular transport. Patients with hereditary renal hypouricemia have a higher risk of exercise-induced acute kidney injury (EAKI) and reduced kidney function. Although the best preventive measure is avoiding exercise, there are many kinds of jobs that require occupational exercise. A 27-year-old male police officer suffered from stage 3 AKI after performing a 20-m multistage shuttle run test. His mother had previously been diagnosed as having renal hypouricemia at another facility. The patient had reported having hypouricemia during a health check at a previous police station, but his serum uric acid concentration was within the normal range at our hospital. After treatment, he recovered from EAKI and exhibited low serum uric acid and hyper-uric acid clearance. Since the patient desired to continue his career requiring strenuous exercise, it was difficult to establish a preventive plan against the recurrence of EAKI. Patients with hereditary renal hypouricemia who must undergo strenuous occupational anaerobic exercise are at higher risk of developing EAKI than other workers. The risks of EAKI among patients with hypouricemia should be considered when undergoing physical occupational training.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Exercise; Hereditary renal hypouricemia; Police officer.
Copyright © 2019 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Ichida K, Hosoyamada M, Hisatome I, Enomoto A, Hikita M, Endou H, et al. Clinical and molecular analysis of patients with renal hypouricemia in Japan-influence of URAT1 gene on urinary urate excretion. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Jan;15((1)):164–73. - PubMed
-
- Nishizaki N, Fujinaga S, Hirano D, Kanai H, Kaya H, Ohtomo Y, et al. Hereditary renal hypouricemia: a cause of calcium oxalate urolithiasis in a young female. Clin Nephrol. 2012 Feb;77((2)):161–3. - PubMed
-
- Yan MT, Cheng CJ, Chen JS, Lin SH. The case: a young man with acute kidney injury after exercise. The diagnosis: exercise induced acute kidney injury in hereditary renal hypouricemia. Kidney Int. 2010 May;77((10)):935–6. - PubMed
-
- Fujinaga S, Ito A, Nakagawa M, Watanabe T, Ohtomo Y, Shimizu T. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome with exercise-induced acute kidney injury in renal hypouricemia type 1. Eur J Pediatr. 2013 Nov;172((11)):1557–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

