Automated multiparametric localization of prostate cancer based on B-mode, shear-wave elastography, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound radiomics
- PMID: 31602512
- PMCID: PMC6957554
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-019-06436-w
Automated multiparametric localization of prostate cancer based on B-mode, shear-wave elastography, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound radiomics
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to assess the potential of machine learning based on B-mode, shear-wave elastography (SWE), and dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound (DCE-US) radiomics for the localization of prostate cancer (PCa) lesions using transrectal ultrasound.
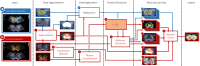
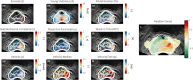
Methods: This study was approved by the institutional review board and comprised 50 men with biopsy-confirmed PCa that were referred for radical prostatectomy. Prior to surgery, patients received transrectal ultrasound (TRUS), SWE, and DCE-US for three imaging planes. The images were automatically segmented and registered. First, model-based features related to contrast perfusion and dispersion were extracted from the DCE-US videos. Subsequently, radiomics were retrieved from all modalities. Machine learning was applied through a random forest classification algorithm, using the co-registered histopathology from the radical prostatectomy specimens as a reference to draw benign and malignant regions of interest. To avoid overfitting, the performance of the multiparametric classifier was assessed through leave-one-patient-out cross-validation.
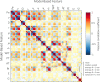
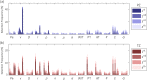
Results: The multiparametric classifier reached a region-wise area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (ROC-AUC) of 0.75 and 0.90 for PCa and Gleason > 3 + 4 significant PCa, respectively, thereby outperforming the best-performing single parameter (i.e., contrast velocity) yielding ROC-AUCs of 0.69 and 0.76, respectively. Machine learning revealed that combinations between perfusion-, dispersion-, and elasticity-related features were favored.
Conclusions: In this paper, technical feasibility of multiparametric machine learning to improve upon single US modalities for the localization of PCa has been demonstrated. Extended datasets for training and testing may establish the clinical value of automatic multiparametric US classification in the early diagnosis of PCa.
Key points: • Combination of B-mode ultrasound, shear-wave elastography, and contrast ultrasound radiomics through machine learning is technically feasible. • Multiparametric ultrasound demonstrated a higher prostate cancer localization ability than single ultrasound modalities. • Computer-aided multiparametric ultrasound could help clinicians in biopsy targeting.
Keywords: Contrast media; Elasticity imaging techniques; Machine learning; Prostate cancer; Ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: Philips.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiparametric ultrasound: evaluation of greyscale, shear wave elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound for prostate cancer detection and localization in correlation to radical prostatectomy specimens.BMC Urol. 2018 Nov 8;18(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12894-018-0409-5. BMC Urol. 2018. PMID: 30409150 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Multiparametric Ultrasound for Prostate Cancer Detection and Localization: Correlation of B-mode, Shear Wave Elastography and Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound with Radical Prostatectomy Specimens.J Urol. 2019 Dec;202(6):1166-1173. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000415. Epub 2019 Jun 27. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 31246546
-
Can 3D Multiparametric Ultrasound Imaging Predict Prostate Biopsy Outcome?Ultrasound Med Biol. 2024 Aug;50(8):1194-1202. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2024.04.007. Epub 2024 May 11. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38734528
-
Multiparametric MRI in detection and staging of prostate cancer.Dan Med J. 2017 Feb;64(2):B5327. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28157066 Review.
-
Ultrasound modalities and quantification: developments of multiparametric ultrasonography, a new modality to detect, localize and target prostatic tumors.Curr Opin Urol. 2015 May;25(3):191-7. doi: 10.1097/MOU.0000000000000162. Curr Opin Urol. 2015. PMID: 25695792 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning based on radiomics features combing B-mode transrectal ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound to improve peripheral zone prostate cancer detection.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024 Jan;49(1):141-150. doi: 10.1007/s00261-023-04050-5. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2024. PMID: 37796326 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of Prostate Lesions Using Transrectal Shear Wave Elastography (SWE) Ultrasound Imaging: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 2;13(1):122. doi: 10.3390/cancers13010122. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33558449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiomic Pipelines for Prostate Cancer in External Beam Radiation Therapy: A Review of Methods and Future Directions.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 3;13(13):3907. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133907. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of high-risk prostate cancer based on the habitat features of biparametric magnetic resonance and the omics features of contrast-enhanced ultrasound.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 16;10(18):e37955. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37955. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39323806 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of multiparametric ultrasound in the diagnosis of prostate cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis.Insights Imaging. 2023 Nov 24;14(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01543-1. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 38001351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

