Differential Clinical Significance of Neurotrophin-3 Expression according to MYCN Amplification and TrkC Expression in Neuroblastoma
- PMID: 31602824
- PMCID: PMC6786962
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e254
Differential Clinical Significance of Neurotrophin-3 Expression according to MYCN Amplification and TrkC Expression in Neuroblastoma
Abstract
Background: Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), a member of the NT family, has only been considered an ancillary compound that provides anti-apoptotic benefits by inactivating tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC)-induced apoptotic signals. However, little is known about the clinical relevance of NT-3 expression itself in neuroblastoma. The purpose of this study was to assess NT-3 expression in patients with neuroblastoma and its relevance to clinicopathologic findings and treatment outcomes.
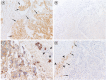
Methods: In this study, expression of NT-3 and TrkC was analyzed using immunohistochemistry in 240 patients with newly diagnosed neuroblastoma.
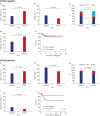
Results: The results of the study revealed that NT-3 expression was associated with older age at diagnosis, localized tumors, and more differentiated tumors but was not associated with early treatment response (degree of residual tumor volume after three cycles of chemotherapy) and progression-free survival (PFS). However, when analysis was confined to patients with MYCN amplified tumors, NT-3 expression was associated with better early treatment response with borderline significance (P = 0.092) and higher PFS (86.9% vs. 58.2%; P = 0.044). In multivariate analysis in patients with MYCN amplified tumors, NT-3 was independent prognostic factor (hazard ratio, 0.246; 95% confidence interval, 0.061-0.997; P = 0.050). In another subgroup analysis, the early treatment response was better if NT-3 was expressed in patients without TrkC expression (P = 0.053) while it was poorer in patients with TrkC expression (P = 0.023).
Conclusion: This study suggests that NT-3 expression in neuroblastoma has its own clinical significance independent of TrkC expression, and its prognostic significance differs depending on the status of MYCN amplification and/or TrkC expression.
Keywords: MYCN; Neuroblastoma; Neurotrophin-3; TrkC.
© 2019 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Lee JW, Son MH, Cho HW, Ma YE, Yoo KH, Sung KW, et al. Clinical significance of MYCN amplification in patients with high-risk neuroblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018;65(10):e27257. - PubMed
-
- Maris JM, Hogarty MD, Bagatell R, Cohn SL. Neuroblastoma. Lancet. 2007;369(9579):2106–2120. - PubMed
-
- Herr I, Debatin KM. Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood. 2001;98(9):2603–2614. - PubMed
-
- Fisher DE. Apoptosis in cancer therapy: crossing the threshold. Cell. 1994;78(4):539–542. - PubMed
-
- Gaynon PS, Desai AA, Bostrom BC, Hutchinson RJ, Lange BJ, Nachman JB, et al. Early response to therapy and outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a review. Cancer. 1997;80(9):1717–1726. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

