BDNF downregulates β-adrenergic receptor-mediated hypotensive mechanisms in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
- PMID: 31603352
- PMCID: PMC6962618
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00478.2019
BDNF downregulates β-adrenergic receptor-mediated hypotensive mechanisms in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
Abstract
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is upregulated in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) in response to hypertensive stimuli such as stress and hyperosmolality, and BDNF acting in the PVN plays a key role in elevating sympathetic activity and blood pressure. However, downstream mechanisms mediating these effects remain unclear. We tested the hypothesis that BDNF increases blood pressure, in part by diminishing inhibitory hypotensive input from nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) catecholaminergic neurons projecting to the PVN. Male Sprague-Dawley rats received bilateral PVN injections of viral vectors expressing either green fluorescent protein (GFP) or BDNF and bilateral NTS injections of vehicle or anti-dopamine-β-hydroxylase-conjugated saporin (DSAP), a neurotoxin that selectively lesions noradrenergic and adrenergic neurons. BDNF overexpression in the PVN without NTS lesioning significantly increased mean arterial pressure (MAP) in awake animals by 18.7 ± 1.8 mmHg. DSAP treatment also increased MAP in the GFP group, by 9.8 ± 3.2 mmHg, but failed to affect MAP in the BDNF group, indicating a BDNF-induced loss of NTS catecholaminergic hypotensive effects. In addition, in α-chloralose-urethane-anesthetized rats, hypotensive responses to PVN injections of the β-adrenergic agonist isoprenaline were significantly attenuated by BDNF overexpression, whereas PVN injections of phenylephrine had no effect on blood pressure. BDNF treatment was also found to significantly reduce β1-adrenergic receptor mRNA expression in the PVN, whereas expression of other adrenergic receptors was unaffected. In summary, increased BDNF expression in the PVN elevates blood pressure, in part by downregulating β-receptor signaling and diminishing hypotensive catecholaminergic input from the NTS to the PVN.NEW & NOTEWORTHY We have shown that BDNF, a key hypothalamic regulator of blood pressure, disrupts catecholaminergic signaling between the NTS and the PVN by reducing the responsiveness of PVN neurons to inhibitory hypotensive β-adrenergic input from the NTS. This may be occurring partly via BDNF-mediated downregulation of β1-adrenergic receptor expression in the PVN and results in an increase in blood pressure.
Keywords: blood pressure; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; catecholamine; hypothalamus; β-adrenergic receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures




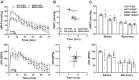
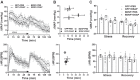
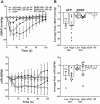

References
-
- Aliaga E, Arancibia S, Givalois L, Tapia-Arancibia L. Osmotic stress increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA expression in the hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus with differential regulation of its transcripts. Relation to arginine-vasopressin content. Neuroscience 112: 841–850, 2002. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(02)00128-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

