Development of ASAS quality standards to improve the quality of health and care services for patients with axial spondyloarthritis
- PMID: 31604704
- PMCID: PMC7025729
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216034
Development of ASAS quality standards to improve the quality of health and care services for patients with axial spondyloarthritis
Abstract
Objectives: The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) aimed to develop a set of quality standards (QS) to help improve the quality of healthcare provided to adult patients affected by axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) worldwide.
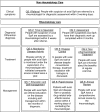
Methods: An ASAS task force developed a set of QS using a stepwise approach. First, key areas for quality improvement were identified, discussed, rated and agreed on. Thereafter, areas were prioritised and statements for the most important key areas were phrased on consensus. Appropriate quality measures were defined to allow quantification of the QS at the community level.
Results: The ASAS task force, consisting of 20 rheumatologists, two physiotherapists and two patients, selected and proposed 34 potential key areas for quality improvement which were then commented by 140 ASAS members and patients. Within that process three new key areas came up, which led to a re-evaluation of all 37 key areas by 120 ASAS members and patients. Five key areas were identified as most important to determine quality of care: referral including rapid access, rheumatology assessment, treatment, education/self-management and comorbidities. Finally, nine QS were agreed on and endorsed by the whole ASAS membership.
Conclusions: ASAS successfully developed the first set of QS to help improving healthcare for adult patients with axSpA. Even though it may currently not be realistic to achieve the QS in all healthcare systems, they provide high-quality of care framework for patients with axSpA that should be aimed for.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis; quality Indicators; spondyloarthritis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AB received research grants to her department from Abbvie and Celgene and honoraria for lectures or consulting fees form UCB, Janssen, Sandoz, Novartis and Eli-Lilly. JB: honoraria for talks, advisory boards, paid consultancies and grants from studies from Abbvie, Amgen, BMS, Boehringer, Celgene, Celltrion, Centocor, Chugai, EBEWE Pharma, Medac, MSD (Schering-Plough), Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer (Wyeth), Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, UCB. PC: honoraria for talks, advisory boards, paid consultancies from Celgene, MSD (Schering-Plough), Novartis, Pfizer (Wyeth), Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, UCB. MD: honoraria for lectures and advisory board meetings for Pfizer, Abbvie, Merck, UCB, Lilly, Novartis. LG research grants: Pfizer, UCB, Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb; honoraria for lectures and advisory board meetings from AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celgene, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, Sanofi-Aventis, UCBU. UK: received grant and research support and consultancy fees from AbbVie, Biogen, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Grünenthal, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and UCB. RBML: honoraria for lectures and advisory board meetings for AbbVie, Celgene, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCBP. PMM has received consulting/speaker’s fees from Abbvie, BMS, Celgene, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and UCB. HM-O: grants from Janssen, Novartis. Speaking, honoraria from Abbvie, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB. AM: honoraria for lectures and advisory board meetings for AbbVie, BMS, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Sanofi, Pfizer and UCB.VN-C: consultancy/speaker/research grants from: Abbvie, BMS, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB. educational/research grants: SAR, SER, SORCOM, EULAR, ASAS. MR: honoraria for presentations or advisory board meetings from Abbvie, Celgene, BMS, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB. PS-B: honoraria for presentations or advisory board meetings from Abbvie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Novartis, UCB. GS: honoraria for lectures and/or advisory board meetings from Abbvie, Lilly, Novartis, Sanofi, Roche. DvdH: consulting fees AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Daiichi, Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, UCB Pharma. Director of Imaging Rheumatology AvT received research grants from Pfizer, Abbvie, UCB, Novartis and Biogen and consulting fees from Novartis, Jansen-Cilag, Pfizer, MW: consulting fees from Novartis, Lilly, UCB.
Figures
References
-
- Sørensen J, Hetland ML, All Departments of Rheumatology in Denmark . Diagnostic delay in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: results from the Danish nationwide DANBIO registry. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:e12 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204867 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials