Local ancestry at APOE modifies Alzheimer's disease risk in Caribbean Hispanics
- PMID: 31606368
- PMCID: PMC6925639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2019.07.016
Local ancestry at APOE modifies Alzheimer's disease risk in Caribbean Hispanics
Abstract
Introduction: Although the relationship between APOE and Alzheimer's disease (AD) is well established in populations of European descent, the effects of APOE and ancestry on AD risk in diverse populations is not well understood.
Methods: Logistic mixed model regression and survival analyses were performed in a sample of 3067 Caribbean Hispanics and 3028 individuals of European descent to assess the effects of APOE genotype, local ancestry, and genome-wide ancestry on AD risk and age at onset.
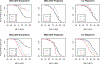
Results: Among the Caribbean Hispanics, individuals with African-derived ancestry at APOE had 39% lower odds of AD than individuals with European-derived APOE, after adjusting for APOE genotype, age, and genome-wide ancestry. While APOE E2 and E4 effects on AD risk and age at onset were significant in the Caribbean Hispanics, they were substantially attenuated compared with those in European ancestry individuals.
Discussion: These results suggest that additional genetic variation in the APOE region influences AD risk beyond APOE E2/E3/E4.
Keywords: APOE; Admixture; Age at onset; Alzheimer's disease; Ancestry.
Copyright © 2019 the Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Lane CA, Hardy J, Schott JM. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol. 2017. - PubMed
-
- Gatz M, Reynolds CA, Fratiglioni L, Johansson B, Mortimer JA, Berg S, et al. Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:168–74. - PubMed
-
- Goate A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Mullan M, Brown J, Crawford F, Fidani L, et al. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1991;349:704–6. - PubMed
-
- Sherrington R, Rogaev EI, Liang Y, Rogaeva EA, Levesque G, Ikeda M, et al. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1995;375:754–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

